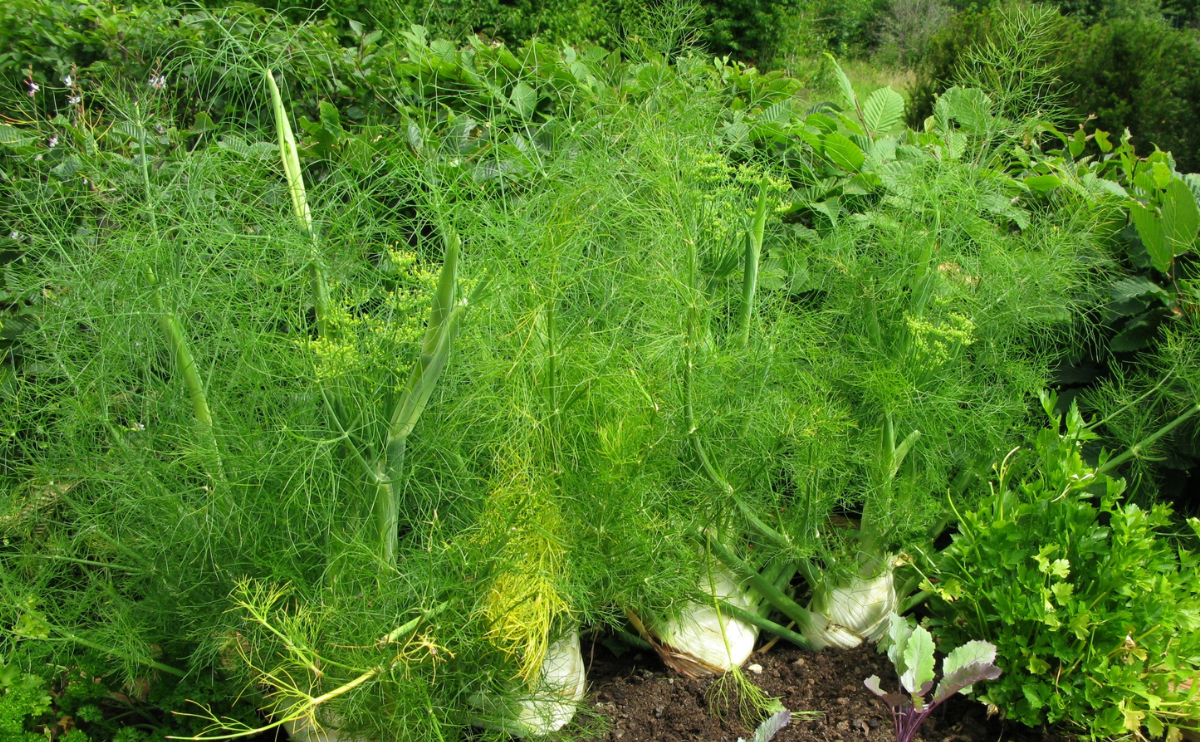
Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) is a perennial herb grown both for culinary purposes and for its ornamental value. Its feathery, branching, aromatic, yellow-green foliage and tall stature can be attractive as border plantings, in cottage gardens, and more. It is also a good choice for butterfly gardens, as swallowtail caterpillars use it as a food source and pupal site. The plant sports small yellow flowers in the summertime, followed by aromatic seeds that can be harvested along with the foliage. It has a flavor similar to anise or licorice. Fennel is typically planted in the spring, and it has a fast growth rate.

| Common Name | Fennel, sweet fennel, common fennel |
| Botanical Name | Foeniculum vulgare |
| Family | Apiaceae |
| Plant Type | Perennial, herb |
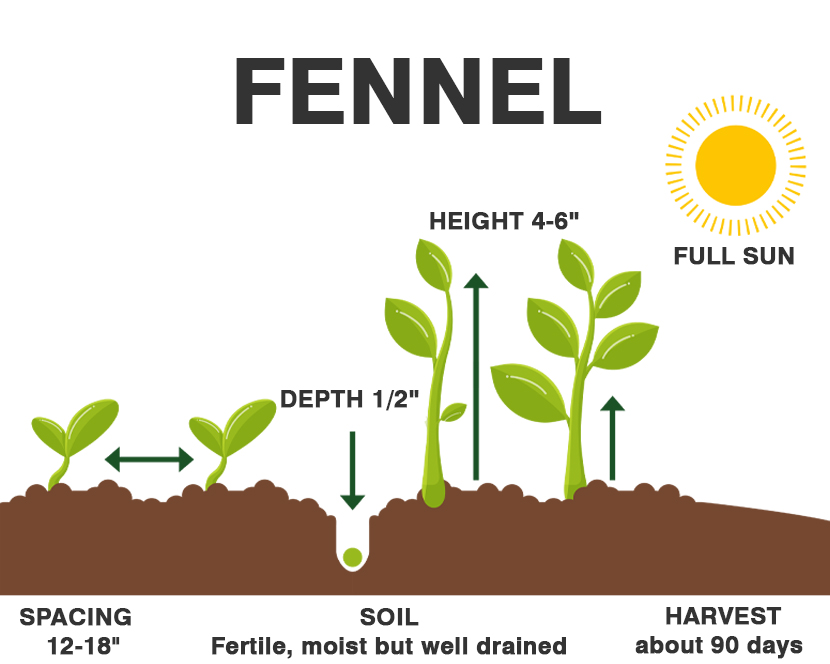
| Size | 4–6 feet tall, 1.5–3 ft. wide |
| Sun Exposure | Full sun |
| Soil Type | Moist, well-drained |
| Soil pH | Acidic (5.5–6.8) |
| Bloom Time | Summer |
| Hardiness Zones | 4–9 (USDA) |
| Native Area | Mediterranean |

When to Plant?
This will be determined by your planting zone. There is a final frost date for each area. As a result, you can plan your gardening activities around this date. Check our Frost Dates Across North America: First & Last Frost Dates Chart. However, the date will not be the same for every plant.
How to Plant
You’ll find two methods of propagation when researching how to grow fennel. Plants may be divided, but this isn’t as easy as it is with other garden plants and often proves unsatisfactory. This is because the fennel has a long taproot that doesn’t like to be divided or moved. Planting fennel by seed is a much easier option.
Seeds can be sown as soon as the soil warms in the spring. Soaking your seeds for a day or two before sowing will ensure better germination.
Keep the area moist until the seeds sprout, and thin the fennel plants to 12 to 18 inches (31-46 cm.) apart when they are 4 to 6 inches (10-15 cm.) tall. Plants will begin flowering about 90 days after planting.
Fennel is a highly aromatic and slightly odd plant. The bulb can be grilled until tender, or sliced thin for use in slaws and salads. Fennel companion planting generally only works when growing dill. However, even dill is a poor choice because the two herbs tend to cross-pollinate.
How to Cultivate
Soil – It prefers moist, well-drained soil but can grow in clay.
Sun – Full sun
Spacing – 12 – 18″
Water – Moist to dry (it’s adaptable)
Let the soil dry out completely before watering.
Fertilizer – This plant has no special fertilizing needs
How to Harvest
Fennel is ready to harvest after approximately 90 days. Fennel leaves can be harvested as soon as the plant is well established. Only take a few leaves at a time to not cause harm to the plant. The bulb is ready for harvest once it reaches the size of a tennis ball. To harvest the bulb, cut the fronds from the base of the bulb.
Hydroponics
Germination: Fennel seeds can be germinated in a seedling tray filled with hydroponic growing media, such as rockwool cubes or coco coir. The seeds should be planted about 1/4 inch deep and kept moist until they sprout, which typically takes 1-2 weeks.
pH range: The pH range for hydroponic fennel should be between 6.0-7.0. Maintaining the correct pH level is important for the plants to absorb the necessary nutrients.
EC: Fennel prefers a low to medium electrical conductivity (EC) level, with a general guideline of maintaining an EC between 1.2-2.2 mS/cm.
PPM: The parts per million (PPM) for hydroponic fennel should be around 600-1200 ppm. This measures the concentration of nutrients in the water solution.
Humidity: The humidity level should be maintained at around 50-70% for fennel to grow properly. This can be achieved by using a humidifier or by placing a tray of water near the plants.
Light hours: Fennel requires at least 6-8 hours of light per day to grow properly. Ideally, provide 12-16 hours of light per day using a grow light with a spectrum suitable for vegetative growth.
Air temperature: Fennel grows best in temperatures between 60-70°F (15-21°C). Keep the air temperature in your growing area within this range using a heater or air conditioning unit if necessary.
Water temperature: The water temperature in your hydroponic system should be maintained between 60-70°F (15-21°C). Use a water heater or chiller to adjust the water temperature as needed.
By following these guidelines, you should be able to successfully grow fennel hydroponically. Good luck with your growing!