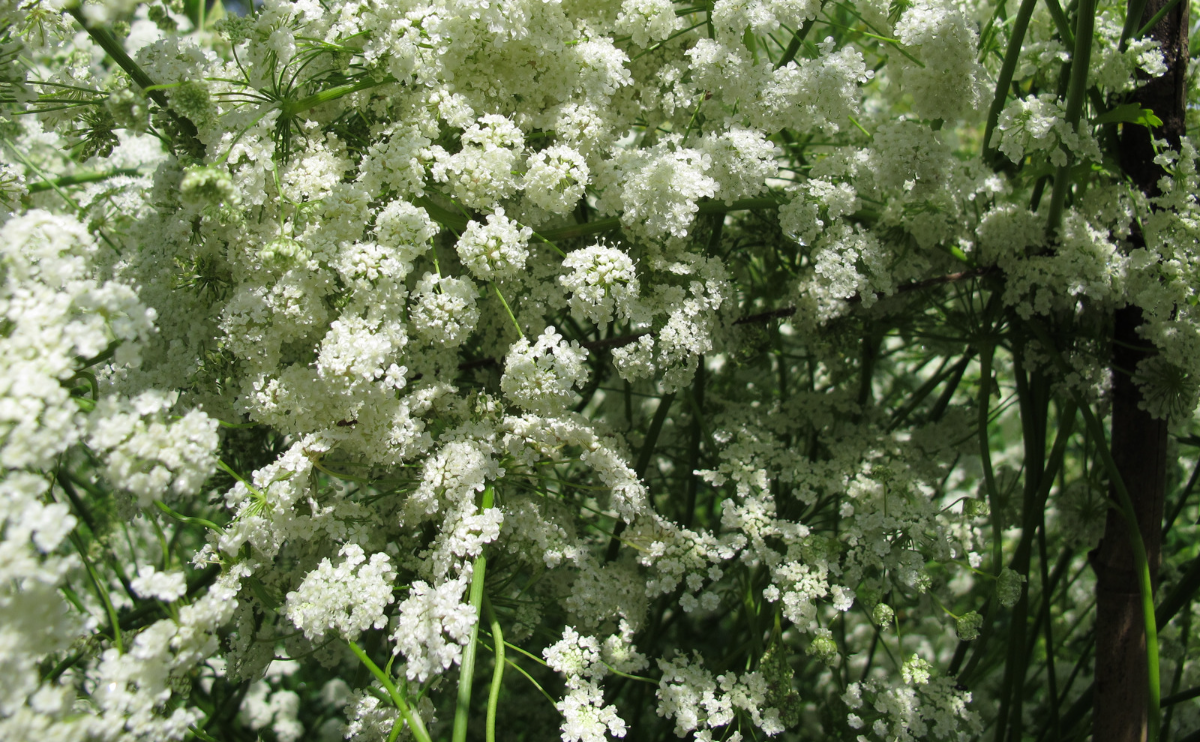
Anise (Pimpinella anisum), also called aniseed or rarely anix is a flowering plant in the family Apiaceae native to the eastern Mediterranean region and Southwest Asia.
The flavor and aroma of its seeds have similarities with some other spices and herbs, such as star anise, fennel, licorice, and tarragon. It is widely cultivated and used to flavor food, candy, and alcoholic drinks, especially around the Mediterranean.

| Botanical Name | Pimpinella anisum |
| Common Name | aniseed, anix |
| Plant Type | Herbaceous annual |
| Mature Size | 60–90 centimetres (2–3 feet) |
| Sun Exposure | Full sun |
| Soil Type | Fertile Chalk, Loam, Sand (not heavy clay, which doesn’t drain well and causes winter problems) |
| Soil pH | Neutral |
| Bloom Time | Mid-summer to fall |
| Flower Color | Creamy white |
| Hardiness Zones | 3-8, USDA |
| Native Area | Mediterranean region and Southwest Asia |

When to Plant?
This will be determined by your planting zone. There is a final frost date for each area. As a result, you can plan your gardening activities around this date. Check our Frost Dates Across North America: First & Last Frost Dates Chart. However, the date will not be the same for every plant.
How to Plant
Grow anise in full sun. Plant anise in a sheltered location out of the wind. Anise grows best in well-drained soil rich in organic matter; however, anise will grow in poor soil. Anise prefers a soil pH of 6.0 to 6.7. Anise tolerates dry conditions but will not tolerate very wet soil.
Start anise from seed indoors in late winter about 8 weeks before transplanting seedlings outdoors. Sow seed in biodegradable pots that can be set out in the garden after the last frost in spring. Keep seeds at 70 °F for optimal germination. Anise forms a tap root that does not like transplanting or moving.
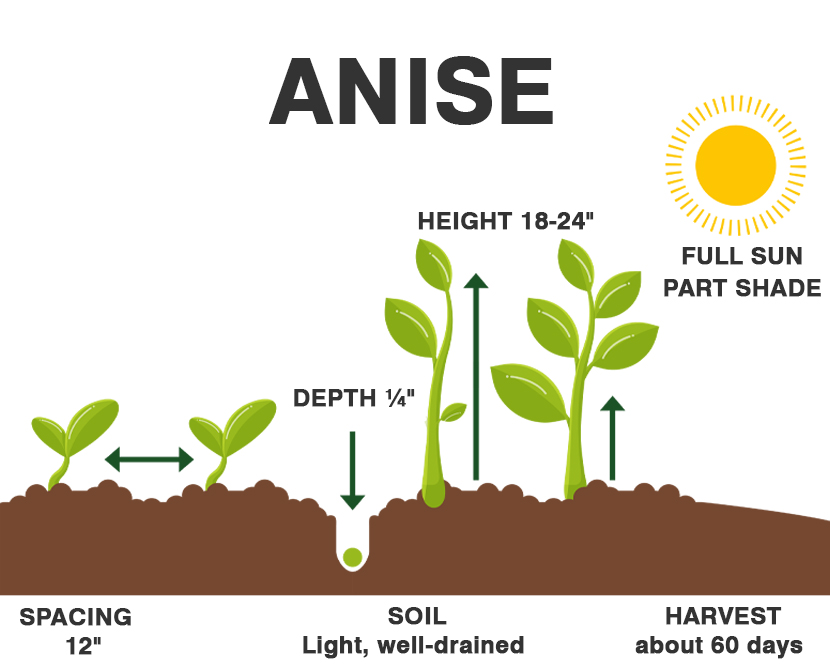
Because anise has a tap root it does not transplant well after the roots become established. Set seedlings in the garden in spring as soon as the soil can be worked; protect young plants with floating row covers or a plastic tunnel until after the last frost.
Sow anise in the garden as early as two weeks before the average last frost date in spring. Anise requires a long, frost-free growing season of about 120 days. Sow anise seeds ¼ inch; seed germinates in about 20 days. Space plants 6 to 18 inches apart. When seedlings are 6 weeks old thin plants to 18 inches apart or more. Grow 6 anise plants for fresh leaves and cooking; grow 12 plants for seeds and preserving.
Anise leaves and seeds have a rich licorice flavor. Add chopped fresh leaves to salads and fruits or use them as a garnish. Use whole, ground, or crushed leaves in baked goods, apple dishes, pickles curries, eggs, or soups. Anise seeds add flavor to sweet rolls and gourmet bread; crushed seeds enhance the flavor of desserts and fresh fruit salads. Seeds intensify the sweetness in pastries, cakes, and cookies Anise is complemented by cinnamon and bay. Anise is said to encourage cilantro to germinate. The strong smell of anise is said to repel aphids and fleas. Avoid planting anise with carrots and radishes. Grow creeping thyme at the foot of anise.
How to Cultivate
Soil – It prefers moist, well-drained soil but can grow in clay.
Sun – Full sun to part shade
Spacing – 12″
Water – Moist to dry (it’s adaptable)
Let the soil dry out completely before watering.
Fertilizer – This plant has no special fertilizing needs
How to Harvest
Snip anise leaves for fresh use as needed. Seeds require more than 100 frost-free days to reach harvest. Harvest seeds from late summer to early autumn starting about two to three weeks after flowering when seeds have turned brown and fall easily from the head.
Snip leaves for fresh use. Leaves can be dried on a screen in a cool, dry, dark, airy place.
Cut the flower stems and seed heads and hang the stalks upside down in a warm, dry, shady place. Place a paper bag around the seed heads, so seeds fall into the bag. Thresh seeds when dry or pasteurize them in an oven at 100 °F for 15 minutes. Complete the harvest before the first frost in fall.100 °F
Hydroponics
Germination: Anise seeds can be germinated in a seedling tray filled with hydroponic growing media, such as rockwool cubes or coco coir. The seeds should be planted about 1/4 inch deep and kept moist until they sprout, which typically takes 1-2 weeks.
pH range: The pH range for hydroponic anise should be between 6.0-7.0. Use a pH meter or test strips to monitor the pH of your nutrient solution and adjust as necessary using pH up or pH down solutions.
EC: Anise prefers a low to medium electrical conductivity (EC) level, with a general guideline of maintaining an EC between 1.2-2.2 mS/cm.
PPM: The parts per million (PPM) for hydroponic anise should be around 600-1200 ppm. This measures the concentration of nutrients in the water solution.
Humidity: Anise prefers a moderate to high humidity level of around 60-70%. Use a hygrometer to monitor the humidity level in your growing area and adjust as necessary using a humidifier.
Light hours: Anise requires at least 6-8 hours of light per day to grow properly. Ideally, provide 12-16 hours of light per day using a grow light with a spectrum suitable for vegetative growth.
Air temperature: The air temperature should be maintained at around 20-25°C (68-77°F) during the day and around 15-18°C (59-64°F) at night for anise to grow well.
Water temperature: The water temperature in your hydroponic system should be maintained between 60-70°F (15-21°C). Use a water heater or chiller to adjust the water temperature as needed.
By following these guidelines, you should be able to successfully grow anise hydroponically. Good luck with your growing!