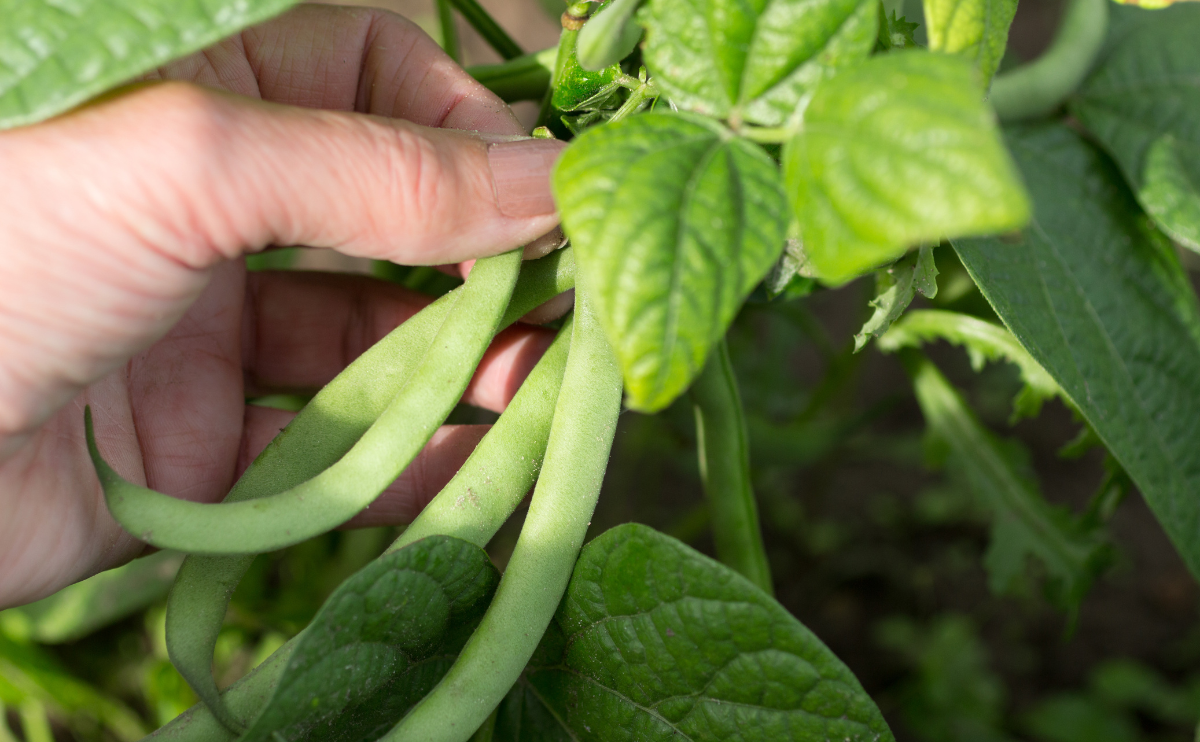
The common bean plant (Phaseolus vulgaris) includes an enormous number of varieties of pod/snap beans that have edible pods, but also shell beans and dry beans, in which the inner seeds are removed from inedible pods before they are prepared and eaten. Most home gardeners will be raising the pod/snap type, which includes both pole bean varieties that grow long vines as well as low-growing bush beans. Most varieties of pod/snap beans are green, but there are also purple, red, yellow, and streaked beans. Common beans are several inches long and either round or flattened in shape.
Bean plants are annual vegetables that grow quickly and are best planted in the spring. The flowers appear about two months after planting. Harvest time varies greatly, depending on the type of bean. Note that the seeds of raw or undercooked beans can be toxic to people and animals.

| Common Name | Common bean, green bean, French bean, snap bean, string bean |
| Botanical Name | Phaseolus vulgaris |
| Family | Fabaceae |
| Plant Type | Annual, vegetable |
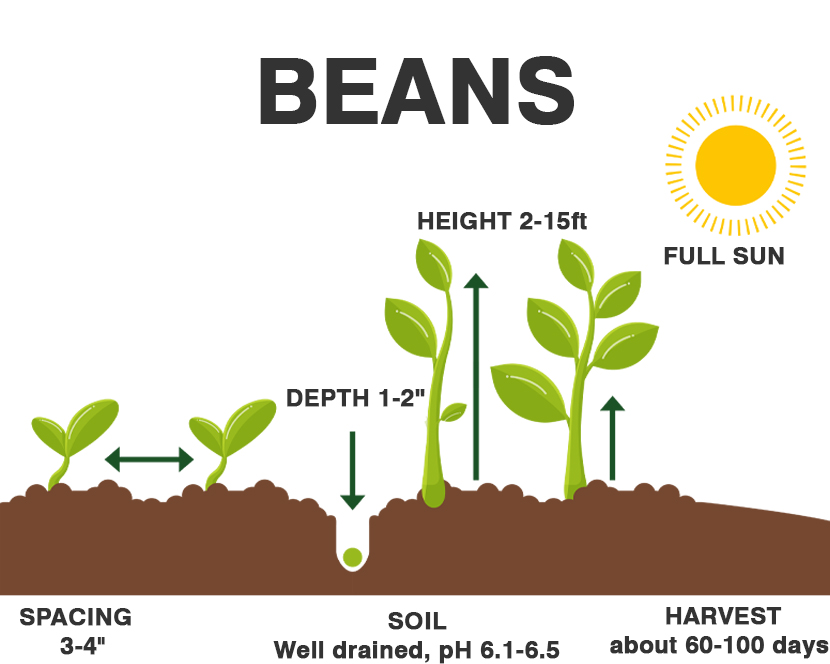
| Size | 2–15 ft. tall, 2–3 ft. wide |
| Sun Exposure | Full sun, |
| Soil Type | Loamy, moist, well-drained |
| Soil pH | Acidic |
| Hardiness Zones | 2–11 (USDA) |
| Native Area | South America, Central America |

When to Plant?
This will be determined by your planting zone. There is a final frost date for each area. As a result, you can plan your gardening activities around this date. Check our Frost Dates Across North America: First & Last Frost Dates Chart. However, the date will not be the same for every plant.
How to Plant
Green bean crops have two growing styles: bush and pole. Bush beans grow out in a compact space, while pole beans grow on climbing vines. Both pole and bush beans need very similar conditions to grow.
Sow seeds directly. Sow green bean seeds directly into your soil, rather than starting the growing process indoors. Bean plants have fragile roots, which makes them difficult to transplant.
Check the temperature. Ensure that soil temperature is at least 50 to 60 degrees Fahrenheit before sowing green bean seeds to prevent slow germination or rot. Green beans are a warm-weather crop, which produces the highest yields in air temperatures between 65 and 80 degrees Fahrenheit.
Support the pole beans. Prior to planting pole beans, you will need to set up either a trellis or a teepee to support the beans as they grow. For the teepee method, gather at least three long branches or wooden poles together that are approximately six to seven feet in height, tying them together at the top, and splaying the bottoms of the supports in a circle. As vines emerge, begin winding them up the poles. This method will train the plant to continue winding throughout the growing season.
Provide enough space. To plant bush bean seeds, sow them about one to one and a half inches deep and three inches apart, with your bean rows 18 inches apart. If you are planting pole beans, plant three or four seeds around each of the poles, four to eight inches apart, in rows that are two to three feet apart.
Green beans are a tender, annual vegetable also known as string beans or snap beans. Green bean plants can grow easily in your vegetable garden, regularly producing large quantities, which are easy to care for and harvest.
Additionally, bean plants should be well-ventilated to promote proper development and deter mildew or mold that can trouble plants.
Beans should not be grown in the same spot more than once every four years, and can be mutually beneficial with corn, strawberries and cucumber.
Avoid planting beans near onion or fennel.
Companions – corn and squash. Since pole and bush beans have different habits, different crops make more suitable companions.
How to Cultivate
Green beans are easy to grow, as they only require light maintenance and care to thrive.
Balance your soil pH. Green beans prefer a slightly acidic soil with a pH of around 6.0. Green beans fix their own nitrogen, so a normal, rich soil can help produce quality plants without fertilization. (However, pole beans may require a supplemental compost halfway through their growing season if they are continuously producing crops).
Provide sun. Green bean plants need six to eight hours of full sun per day. Make sure your plants have access to direct sunlight. However, high temperatures can cause blossoms to fall from your green bean plants, so use row covers to protect plants from high heat. Water properly. Beans require well-drained soil to keep from rotting or creating powdery mildew. Give your bean plants about two inches of water per week. Apply the water to the soil directly to keep your plants nourished.
How to Harvest
Bush beans are generally ready to harvest within 50–55 days, while pole beans can take 55 to 60 days. The bean pods are ready to harvest when they’re four to six inches long and slightly firm, and before the beans protrude through the skin. Gently pull the beans from the plant, taking care not to tear the blooms. Harvest often to promote more sprouting.
Hydroponics
Germination: Soak the bean seeds in water for 24 hours to help soften the outer shell and promote germination. Drain the water and place the seeds in a damp paper towel or cloth. Place the towel or cloth in a dark, warm location for 2-3 days, making sure to keep it moist. Once the seeds have sprouted and developed roots, they are ready to be planted in the hydroponic system.
pH range: The optimal pH range for growing beans hydroponically is between 6.0 and 6.5. It is important to regularly monitor and adjust the pH level of the nutrient solution to ensure optimal growth.
EC: The ideal electrical conductivity (EC) level for bean plants is between 1.0 and 2.5 mS/cm. This can be measured using a handheld EC meter and adjusted as needed.
PPM: The optimal parts per million (PPM) for growing beans hydroponically is between 700 and 1500. This can also be measured using a TDS/PPM meter and adjusted as needed.
Humidity: The ideal humidity level for bean plants is between 50% and 70%. This can be achieved by using a humidifier or dehumidifier depending on the ambient humidity in the growing area.
Light hours: Bean plants require approximately 12-14 hours of light per day to grow properly. A grow light can be used to supplement natural light if needed.
Temperature air: The ideal air temperature for growing beans hydroponically is between 68°F and 78°F (20°C to 25°C).
Temperature water: The optimal water temperature for growing beans hydroponically is between 65°F and 75°F (18°C to 24°C). It is important to monitor the water temperature regularly and adjust as needed to maintain this range.
Overall, growing beans hydroponically can be a rewarding and efficient way to produce fresh, healthy produce. By following these guidelines and regularly monitoring and adjusting nutrient levels and environmental conditions, you can ensure a successful harvest.