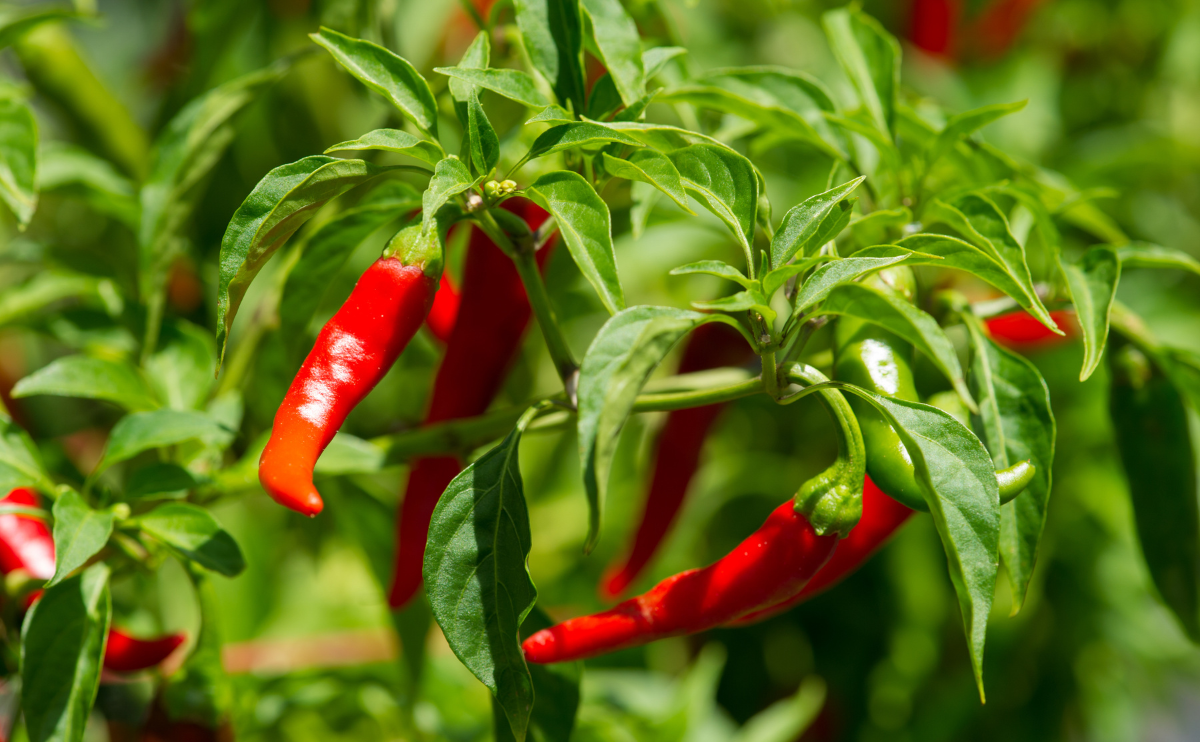
If you want to add a bit of spice to your garden, the cayenne pepper plant might be the perfect choice. This pepper is a Capsicum annuum cultivar. The species includes many other common pepper varieties, such as bell peppers, serrano peppers, and jalapeños. Bushy plants have smooth elliptical green leaves and small white star-shaped flowers. Cayenne peppers are categorized as medium heat. They measure around 4 to 6 inches long and have a tapering shape with a curved tip. They are most commonly a glossy red with a slightly wrinkled texture.
Cayenne pepper plants are frost-tender perennials that are commonly grown as annuals in cold climates. They should be planted in the spring and have a fairly quick growth rate. Note that the fruits, leaves, and seeds of cayenne peppers are technically toxic to people due to the capsaicin compounds.

| Common Name | Cayenne pepper |
| Botanical Name | Capsicum annuum ‘Cayenne’ |
| Family | Solanaceae |
| Plant Type | Perennial, vegetable |
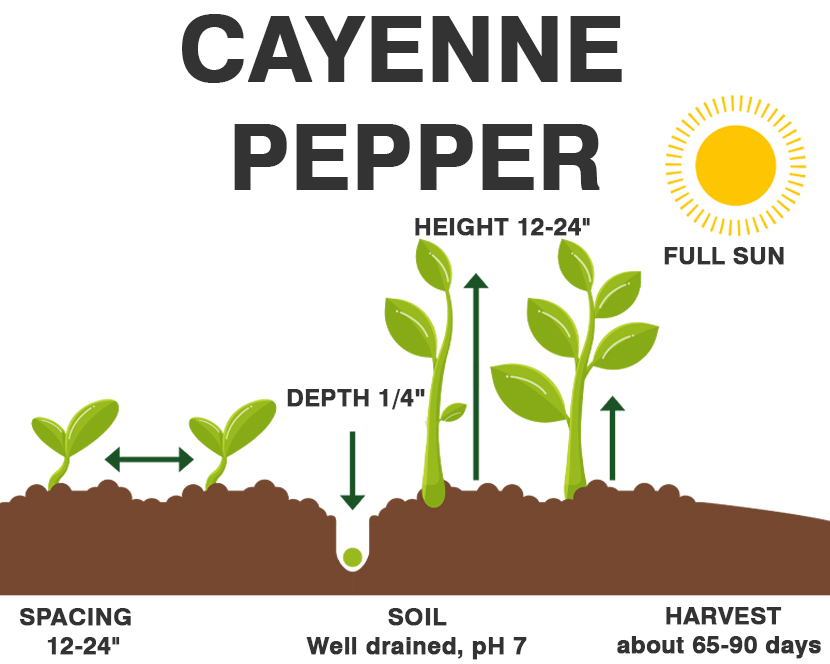
| Size | 1–4 ft. tall, 1–2 ft. wide |
| Sun Exposure | Full sun |
| Soil Type | Moist, well-drained |
| Soil pH | Acidic, neutral |
| Bloom Time | Summer |
| Hardiness Zones | 9–11 (USDA) |
| Native Area | South America, Central America |

When to Plant?
This will be determined by your planting zone. There is a final frost date for each area. As a result, you can plan your gardening activities around this date. Check our Frost Dates Across North America: First & Last Frost Dates Chart. However, the date will not be the same for every plant.
How to Plant
If you want to grow cayenne peppers in your own garden, and you happen to have a longer growing season and plenty of sun, you can sow the seeds directly into the soil 10 to 14 days before the final frost of the year.
However, when starting your cayenne pepper plant, you’ll likely have the most success by planting them indoors or, better yet, in a greenhouse. The seedlings are delicate and cannot tolerate either overly hot or cold conditions.
When starting your plants indoors, place the container in a sunny location in a room that will maintain a temperature of at least 60 degrees Fahrenheit. The seeds should be planted in light, well-drained soil and usually sprout in about 16 to 20 days.
Plant the growing seedlings into flats spaced a few inches apart or in individual pots, and then allow them to gradually acclimate to outdoor temperatures before transplanting about six to eight weeks later (assuming that all danger of frost has passed).
Transplanting is a shock for cayenne pepper seedlings, so take care to minimize the trauma. If you choose to transplant prior to the final frost of the season, you can protect them with hot caps, row covers, or black plastic.
How to Cultivate
The cayenne pepper plant will grow best when exposed to full sunlight for at least eight hours per day. Cayenne pepper plants require moist, well-drained, fertile soil with a neutral pH. More acidic soil can produce peppers that are spicier than normal. If you are unsure, it may be worth conducting a soil pH level test. Watering cayenne pepper plants can be a delicate process. They do require moist soil, but overwatering is a problem too. If the soil becomes either too dry or too saturated, the plant’s foliage can turn yellow. A deep watering every few days at the base of the plant is generally beneficial. Mulching around the plant can be a helpful way to conserve moisture. The cayenne pepper plant is a warm-weather species native to tropical regions, and it requires consistently warm temperatures to survive. These plants cannot withstand extremes in temperatures, either heat or cold. Temperatures consistently below 55 degrees Fahrenheit will result in slow growth and leaf discoloration. Temperatures below 32 degrees Fahrenheit will damage or kill the plants, and nighttime temperatures above 75 degrees Fahrenheit can impact pepper production levels. Cayenne peppers will grow well in rich, fertile soil. If your soil is not particularly rich, and you plan to use a fertilizer, make sure it isn’t one with high nitrogen levels. This will direct energy towards impressive foliar growth rather than fruit production.
How to Harvest
Cayenne peppers are usually ready to harvest anywhere from 70 to 100 days after planting. Ripe peppers will generally be red, around 4-6 inches long, have a waxy skin, and be firm to the touch. Overripe specimens that are soft will not be edible, and although you can eat the peppers when they are still green, they won’t have such a pleasant or intense flavor.
Though the peppers can be pulled from the stem, it’s recommended to snip the peppers from the plant to help prevent any damage. This is important because, when well maintained, you can continue to harvest peppers until the first fall frost.
Once picked, your peppers can be kept in the refrigerator. It is best to use them within a week of harvesting to appreciate the best flavor and nutritional value. The peppers can also be dried and ground into powdered seasoning for use in an array of cuisines.
Hydroponics
Germination: To germinate Cayenne pepper seeds, soak them in water for 24 hours, plant them in a seed tray or small pots filled with a sterile seed-starting mix, and keep the soil moist but not overly wet. Place the tray or pots in a warm and bright location, and within 7-14 days, you should see sprouts emerging from the soil.
pH Range: The ideal pH range for Cayenne pepper plants is between 5.5 and 6.5. It’s important to monitor the pH of your hydroponic solution regularly and make adjustments as needed to keep it within this range.
EC and PPM: The recommended EC (electrical conductivity) range for Cayenne pepper plants is between 1.8 and 2.5 mS/cm, or 1800 to 2500 ppm (parts per million). This will provide the plants with the right balance of nutrients for healthy growth.
Humidity: Cayenne pepper plants prefer a moderate to high humidity level of around 50-70%. This can be achieved by using a humidifier or by placing a tray of water near the plants to increase moisture in the air.
Light Hours: Cayenne pepper plants require at least 6-8 hours of bright, direct light each day to thrive. Ideally, they should receive 12-14 hours of light per day for optimal growth and fruit production. You can use grow lights if you don’t have access to a sunny window or outdoor space.
Temperature Air: Cayenne pepper plants prefer a warm, stable temperature between 68-85°F (20-30°C). Avoid exposing the plants to extreme temperature fluctuations, as this can cause stress and affect growth.
Temperature Water: The hydroponic solution should be kept at a temperature of around 68-75°F (20-24°C) for optimal nutrient uptake and plant growth. Use a water chiller or heater if necessary to maintain a consistent temperature.
With these guidelines, you should be able to grow healthy Cayenne pepper plants hydroponically. Good luck, and happy growing!