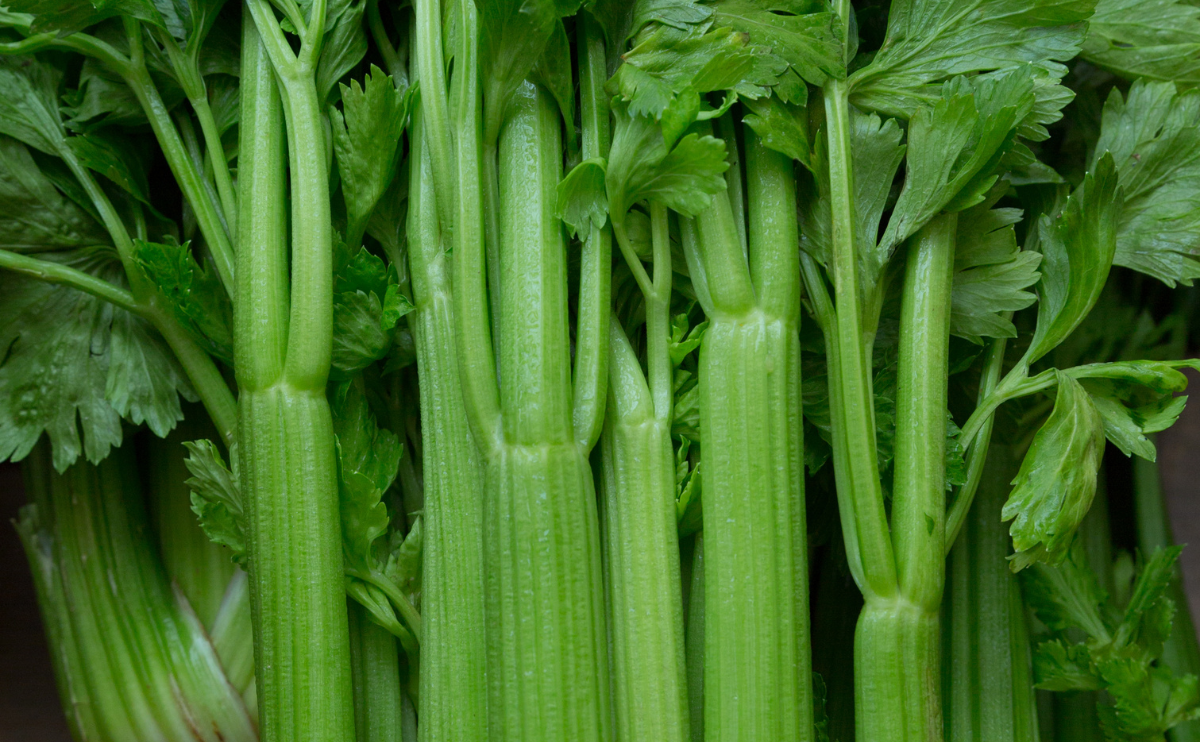
Celery (Apium graveolens) is a marshland plant in the family Apiaceae that has been cultivated as a vegetable since antiquity. Celery has a long fibrous stalk tapering into leaves. Depending on location and cultivar, either its stalks, leaves or hypocotyl are eaten and used in cooking. Celery seed powder is used as a spice.

| Botanical Name | Solanum lycopersicum |
| Common Name | Celery |
| Plant Type | Biennial, vegetable |
| Mature Size | 12- to 18-inch stalks |
| Sun Exposure | Full sun |
| Soil Type | Fertile, well-drained |
| Soil pH | pH: 6.0-6.5 |
| Bloom Time | Spring, fall, early winter |
| Bloom Color | White |
| Hardiness Zones | 2-10, USDA |
| Native Area | Europe, the Mediterranean lands |

When to Plant?
This will be determined by your planting zone. There is a final frost date for each area. As a result, you can plan your gardening activities around this date. Check our Frost Dates Across North America: First & Last Frost Dates Chart. However, the date will not be the same for every plant.
How to Plant
Planting celery seeds indoors starts 8 – 10 weeks before the last spring frost.
Plant the seedlings in the garden 2 – 3 weeks before the average date of the last frost.
In cool spring and summer regions, plant celery in early spring.
In warmer areas, celery can be planted in late summer for late autumn and early winter harvests.
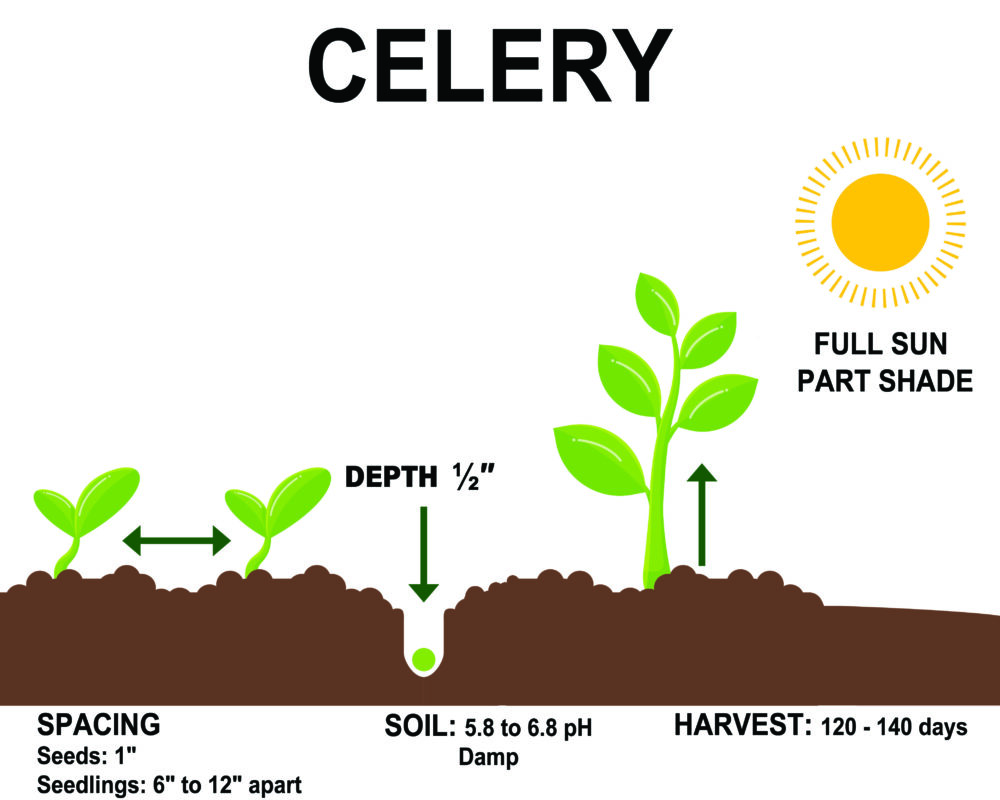
Celery should be grown in compost-rich, water-retaining soil. Celery prefers soils with a pH of 5.8 to 6.8. Celery does not tolerate heat and is best suited to a cool and cloudy place where growing temperatures range from 60°F to 70°F. Celery is best planted where the weather is cool during the growing season of 4 months.
Sow seeds ⅛” deep, spacing plants 6″ to 12″ apart in all directions and with a row spacing of 24 inches. When you set out seedlings, they should reach about 3 inches tall.
Water the celery abundantly during all growth stages, but do not overfill. When celery doesn’t get enough water, it grows slowly.
Add seasoned compost to beds before planting, and cover the plants with compost mid-season.
How to Cultivate
Water – Make sure to provide plenty of water during the entire growing season, especially during hot, dry weather. If celery does not get enough water, the stalks will be dry and small. Add plenty of compost and mulch around the plants to retain moisture.
Soil – 5.8 to 6.8 pH, damp, high fertility
Spacing – seeds – 1″
Seedling – 6″ – 12″
Seed life: 5 years
Sun: Full sun/part shade
Germination: 14 – 21 days, 70°F – 75°F
Day to Harvest: 120 – 140 days
How to Harvest
Harvest the celery before the first heavy frost, when the head is about 2 – 3 inches in diameter at the base and 8 inches in height. You can also harvest it earlier because young celery is as healthful and delicious as a mature product. Harvesting is done by cutting the head off at or slightly below the soil level. Here’s a quick tip: darker stems contain more nutrients.
Hydroponics
Germination: Start by soaking celery seeds in warm water for about 24 hours to soften the seed coat and aid in germination. Prepare a small container with a hydroponic growing medium, such as rockwool cubes or net pots filled with perlite or vermiculite. Plant the seeds in the growing medium, about ¼ inch deep. Keep the container in a warm and humid place until the seeds germinate, which can take up to two weeks.
pH range: Celery grows best in a slightly acidic to neutral pH range of 6.0 to 7.0. You can adjust the pH of your hydroponic system using pH up or pH down solutions to keep it within this range.
EC: The ideal electrical conductivity (EC) range for celery hydroponics is between 1.5 and 2.5 mS/cm. EC measures the total concentration of nutrients in the water, so it’s important to monitor it regularly and adjust as needed.
PPM: The parts per million (PPM) range for celery hydroponics is between 1200 and 1600 ppm. PPM measures the concentration of individual nutrients in the water, so it’s important to ensure that all essential nutrients are present in the right amounts.
Humidity: Celery prefers a relative humidity of 60-70%. Maintaining proper humidity levels can help prevent moisture-related diseases and encourage healthy growth. You can use a humidifier or misting system to maintain the humidity levels in your hydroponic setup.
Light hours: Celery requires 6-8 hours of direct sunlight or artificial light per day. You can use grow lights if your hydroponic setup doesn’t receive enough natural light.
Temperature air: The ideal temperature range for celery hydroponics is between 60°F and 70°F during the day and 55°F and 60°F at night. Avoid exposing your celery plants to temperatures outside of this range to prevent damage and stunted growth.
Temperature water: The water temperature range for celery hydroponics is between 60°F and 75°F. This range ensures that the plants can absorb nutrients and water optimally. You can use a water heater or chiller to adjust the water temperature if necessary.
By following these guidelines, you should be able to grow healthy celery hydroponically. Good luck!