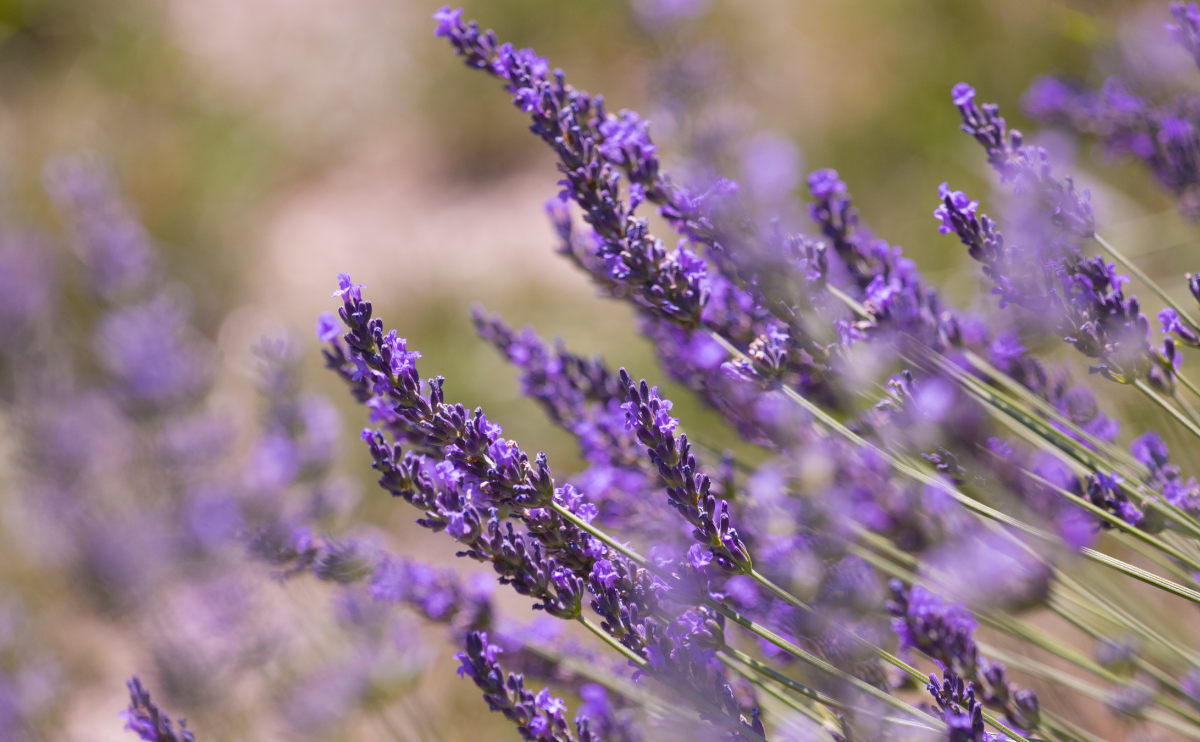
Lavender (Lavendula spp.) is a well-known and fragrant perennial plant that will come back every year with gray-green foliage, upright flower spikes, and a compact shrub form. Planting lavender is best in the spring after the risk of frost has passed and the soil has warmed up. It will grow at a moderate pace, often adding a few inches to its size each year. Lavender can be toxic to pets like dogs and cats.

| Common Name | Lavender |
| Botanical Name | Lavandula spp. |
| Family | Lamiaceae |
| Plant Type | Herbaceous perennial |
| Mature Size | 2–3 ft. tall, 2–4 ft. wide |
| Sun Exposure | Full sun |
| Soil Type | Dry, well-draining |
| Soil pH | Alkaline |
| Bloom Time | Summer |
| Flower Color | Purple |
| Hardiness Zones | 5a–9a, USDA |
| Native Areas | Europe |
| Toxicity | Toxic to dogs, toxic to cats |

When to Plant?
This will be determined by your planting zone. There is a final frost date for each area. As a result, you can plan your gardening activities around this date. Check our Frost Dates Across North America: First & Last Frost Dates Chart. However, the date will not be the same for every plant.
How to Plant
When choosing containers for sowing lavender seedlings, you should give preference to shallow but large and wide containers and boxes.
The container must be at least 12″ in diameter. Container volume should be between 0.5 and 1 gallon. The drainage layer at the bottom of the pot should be at least 1 – 1.5″ high. Lavender seeds are planted one at a time 2 – 3″ apart.
The best time to plant lavender is in spring, from March through May. Lavender can’t tolerate an excess of water in the soil or the air. Good drainage, airflow, and fast-drying stone mulch will ensure a healthy harvest.
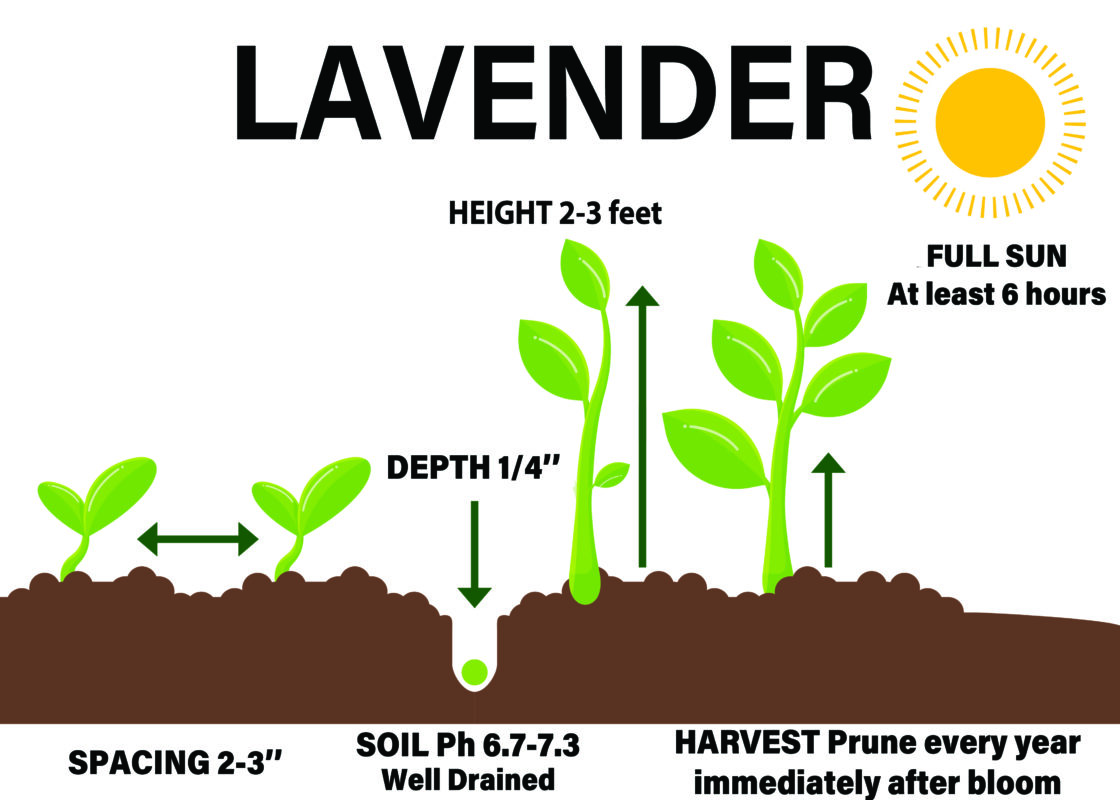
If you live in a southern state where summers are long and hot, then you’ll need to provide slight shade during the peak heat of the day and aid in air circulation by generously spacing out your plants.
The sweetly fragranced perennial herb is a popular ornamental plant for various garden and landscape use. It also has a variety of medicinal and home applications. The essential oils in these plants have various medicinal properties, and they are often used as antiseptics, sleep aids, and stress relief. Lavender is often added to homemade soap, cleaning solutions, lotions, shampoos, and more. Companions – Apple, Rosemary, Cherry, Mint, Agastache, Rose, Sage, Peach, Pear, and Plum.
How to Cultivate
When choosing containers for sowing lavender seedlings, you should give preference to shallow but large and wide containers and boxes.
The container must be at least 12″ in diameter.
Container volume should be between 0.5 and 1 gallon.
The drainage layer at the bottom of the pot should be at least 1 – 1.5″ high.
Lavender seeds are planted one at a time 2 – 3″ apart.
The best time to plant lavender is in spring, from March through May.
Lavender can’t tolerate an excess of water in the soil or the air.
Good drainage, airflow, and fast-drying stone mulch will ensure a healthy harvest.
If you live in a southern state where summers are long and hot, then you’ll need to provide slight shade during the peak heat of the day and aid in air circulation by generously spacing out your plants.
How to Harvest
Soil – Grow in well-drained areas or raised beds.
If you have heavy or clay soil, grow lavender in pots.
If your soil is sandy, mix in some gravel to improve drainage.
An alkaline or especially chalky soil enhances lavender’s fragrance.
Additional feeding is not needed for these plants.
Sun – Ideal conditions – give the plants 6 hours or more of full sun each day.
Full sun to partial afternoon shade, with excellent air circulation.
Water – Lavender is a resilient plant that is extremely drought-tolerant once established.
When first starting your lavender plants, keep them regularly watered during their first growing season.
Spacing – Make sure you have good airflow around the plants if you have high humidity.
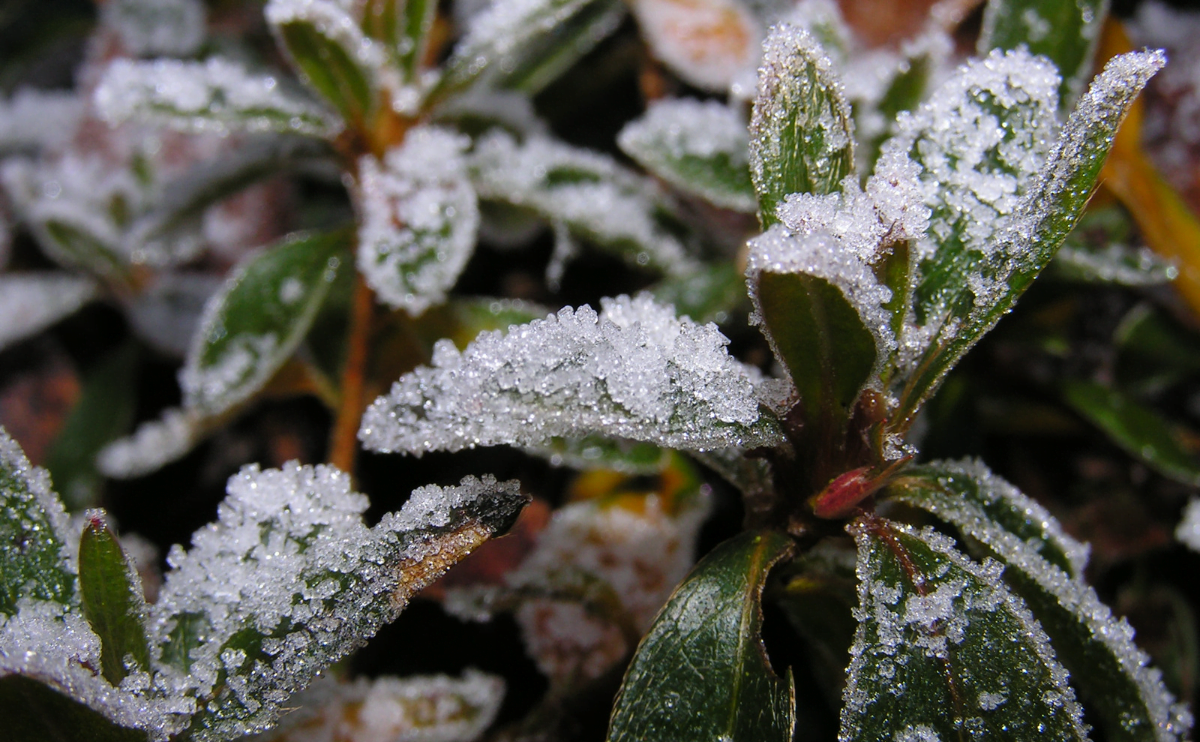
Frost-tolerant – Being a hardy perennial from the Mediterranean, lavender will survive winter temperatures to 0°F.
Hydroponics
Germination: Soak lavender seeds in water for 24 hours before sowing. Place the soaked seeds in a small pot filled with a germination medium like rockwool or coco coir. Water the seeds regularly and keep the pot in a warm and well-lit area. The seeds should germinate in about 2-3 weeks.
pH range: The pH range for hydroponic lavender should be between 6.0-7.5. Maintaining the correct pH level is important for the plants to absorb the necessary nutrients.
EC: The electrical conductivity (EC) level should be maintained at around 1.2-2.4 mS/cm for hydroponic lavender. This helps to ensure that the plants receive the right amount of nutrients.
PPM: The parts per million (PPM) for hydroponic lavender should be around 800-1600 ppm. This measures the concentration of nutrients in the water solution.
Humidity: The humidity level should be maintained at around 40-60% for lavender to grow properly. This can be achieved by using a humidifier or by placing a tray of water near the plants.
Light hours: Lavender requires about 12-14 hours of light per day for optimal growth. You can use artificial lights like LED grow lights to provide the necessary light if natural light is not available.
Temperature air: The air temperature should be maintained at around 18-24°C (65-75°F) during the day and around 15-18°C (60-65°F) at night for lavender to grow well.
Temperature water: The water temperature should be maintained at around 18-22°C (64-72°F) for hydroponic lavender. This helps to ensure that the plants absorb the necessary nutrients.
Overall, growing lavender hydroponically can be a rewarding experience, and following these guidelines can help you grow healthy and vibrant plants.