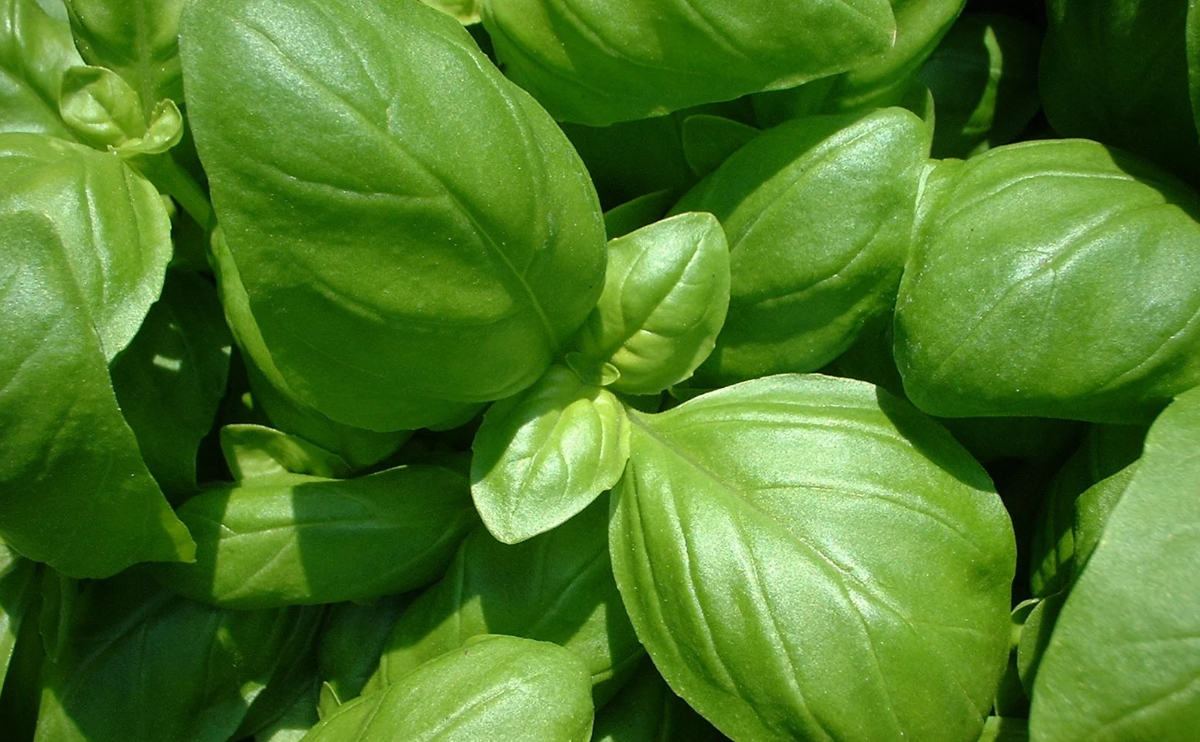
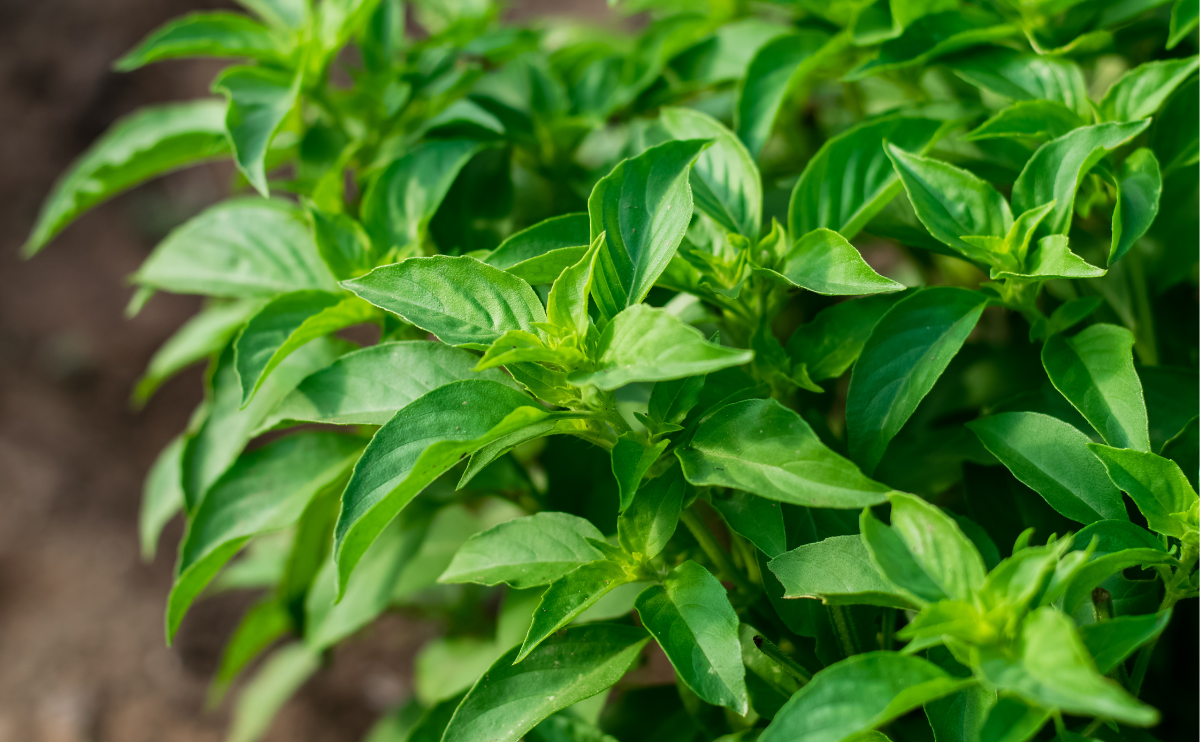
Lemon basil, botanically classified as Ocimum X citriodorum, is a hybrid variety belonging to the Lamiaceae or mint family. The annual plant grows up to 50 centimeters in height and is known for its refreshing and subtly sweet citrus fragrance. Lemon basil is native to Asia, also known as Kemangi in Indonesia, Maenglak in Thailand, and Nasi Ulam in Malaysia, and has remained primarily localized to these regions, used as a fresh, edible garnish. Many Southeast Asian communities harvest the herb straight from wild plants, incorporating the leaves as a flavoring in soups, appetizers, and main dishes. Outside of Asia, Lemon basil is grown as a specialty cultivar in home gardens throughout the United States. The variety is favored as a flavorful addition to ible landscapes, and some farms also grow the cultivar for sale at local farmer’s markets.

| Common Name | Mint |
| Botanical Name | Mentha spp. |
| Family | Lamiaceae |
| Plant Type | Perennial, herb |
| Size | 12–18 in. tall, 18–24 in. wide |
| Sun Exposure | Full, partial |
| Soil Type | Loamy, moist, well-drained |
| Soil pH | Acidic, neutral |
| Bloom Time | Summer |
| Hardiness Zones | 3–11, USA (depends on species) |
| Native Area | North America, Africa, Australia |
| Toxicity | Toxic to animals |

When to Plant?
This will be determined by your planting zone. There is a final frost date for each area. As a result, you can plan your gardening activities around this date. Check our Frost Dates Across North America: First & Last Frost Dates Chart. However, the date will not be the same for every plant.
How to Plant
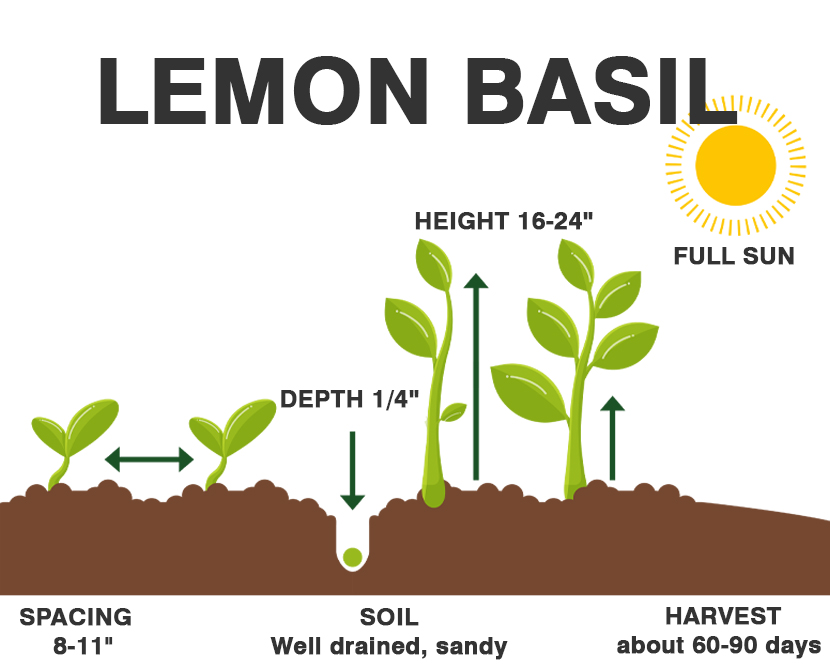
Lemon basil is easy to sow from seed and is relatively quick to germinate. When planting from seed, plant seeds about six weeks before the last frost. Lemon basil is super sensitive to the cold, so whether you are transplanting seedlings from indoors or have plants in the ground, watch the early spring temperatures and cover if necessary. If you are planting a cutting or transplanting a seedling or smaller plant, make sure the ground temperature is at least 70 °F.
In addition to sowing lemon basil from seed, a cutting of basil will easily root when placed in water. Select a four-inch section of lemon basil that has not yet flowered. Roots will form within a week. Transplant the lemon basil directly into the garden or container once a healthy root system is apparent.
Plant basil among other herbs and vegetables with similar lighting and watering needs, like tomatoes or parsley. Some even say tomatoes taste better when they neighbor basil.
Companions – chamomile, lettuce, peppers, and oregano. Keep a few pots of basil on the back porch to deter mosquitoes.
How to Cultivate
Lemon basil does its best in well-drained, moist soil with a neutral pH. Add rich compost to the soil at the beginning of the season. Not much more soil amendment is necessary. In fact, if the soil is too rich, lemon basil loses some of its flavor intensity.
Lemon basil grows well in warm environments that receive about six hours of sun each day.
Give lemon basil water when the soil is dry to the touch, doing your best to water the plant at the base and not all over its leaves.
Depending upon the variety, lemon basil grows anywhere from 12 to 24 inches in height. Space basil plants 12 to 16 inches apart. If you’re limited on space or only grow in containers, consider spicy globe basil, which tends to form a small, mounding habit.
How to Harvest
Lemon basil is a pick-as-you-go kind of herb. You may harvest only what you need, or if you have an abundance on hand, you may clip a mass harvest. Harvest lemon basil as you would mint, snipping a stem just above the point where two large leaves meet. Regular clipping encourages a more rounded, less leggy plant.
It’s always better to harvest lemon basil before the plant flowers. If you don’t have time to harvest any leaves, just pinch off the flowering portion. The flowers are actually edible, but if you pinch them off, the plant can now direct its energy on growing tasty leaves. Also, be sure to only harvest up to 2/3 of the entire plant, so it can continue producing.
Hydroponics
Germination: Start by placing your Lemon basil seeds on top of a moist paper towel and then cover them with another moist paper towel. Keep the paper towels moist and in a warm, dark area. After a few days, the seeds should start to sprout. Once they have sprouted, you can transfer them to your hydroponic setup.
pH Range: The pH range for growing Lemon basil hydroponically should be between 6.0 and 7.0. It’s important to monitor the pH level regularly using a pH meter and adjust it if necessary.
EC: The electrical conductivity (EC) level for growing Lemon basil hydroponically should be between 1.2 and 2.5 mS/cm. This measures the level of nutrients in the water, so it’s important to monitor it regularly using an EC meter.
PPM: The parts per million (PPM) level for growing Lemon basil hydroponically should be between 800 and 1800 ppm. This also measures the level of nutrients in the water, so it’s important to monitor it regularly using a PPM meter.
Humidity: The humidity level for growing Lemon basil hydroponically should be around 50-70%. You can measure the humidity level using a hygrometer and adjust it as necessary by increasing or decreasing the amount of airflow in your grow room.
Light Hours: Lemon basil requires at least 12-16 hours of light per day. You can use LED grow lights or natural sunlight to provide the required amount of light.
Temperature Air: The temperature in the grow room should be around 70-75°F during the day and 60-65°F at night. It’s important to keep the temperature consistent to avoid stress on the plants.
Temperature Water: The temperature of the water should be between 65-75°F. You can use a water heater or chiller to maintain the correct temperature.
In summary, growing Lemon basil hydroponically involves germinating the seeds, monitoring the pH, EC, and PPM levels of the water, controlling the humidity, providing adequate light, and maintaining consistent air and water temperatures. With proper care and attention, you can grow healthy and flavorful Lemon basil using hydroponics.
Common Pests and Diseases
We’ve compiled a list of videos that will teach you how to grow mint.
Related Posts