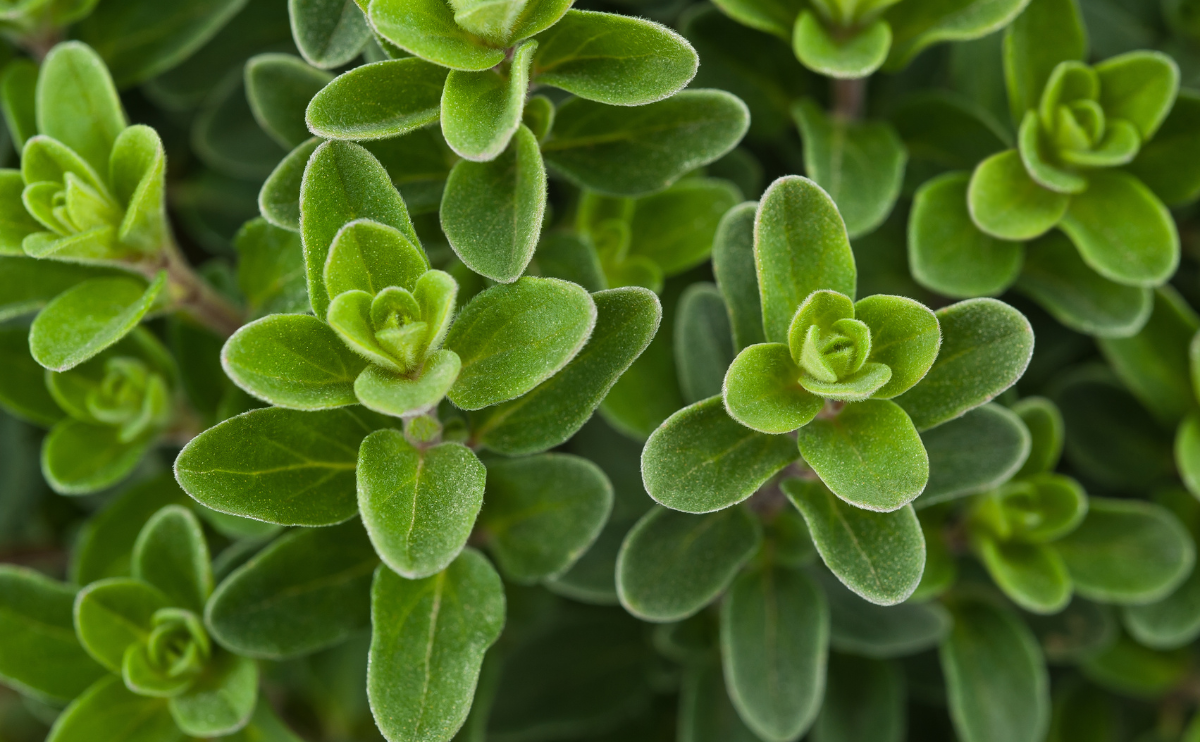
Marjoram (Origanum majorana) is a perennial herb that’s closely related to oregano. It is evergreen in zones 9 and 10, but in most zones it is grown either as an annual or as a potted plant that is brought indoors when the weather turns cold. The low-growing plant has a mounded, shrubby appearance with aromatic, ovate, gray-green leaves that stretch around an inch long. Tiny white or pink flowers bloom from mid- to late summer, though they are not especially showy. Best planted in the spring, marjoram grows slowly and eventually becomes a spreading ground cover. Note that gastrointestinal irritants within marjoram technically make it toxic to humans, as well as to pets

| Common Name | Marjoram, sweet marjoram, knotted marjoram |
| Botanical Name | Origanum majorana |
| Family | Lamiaceae |
| Plant Type | Herbaceous, perennial |
| Size | 1–2 ft. tall, 1–2 ft. wide |
| Sun Exposure | Full sun |
| Soil Type | Sandy, loamy, well-drained |
| Soil pH | Acidic, neutral (6.5–7.5) |
| Bloom Time | Summer |
| Hardiness Zones | 9–10 (USDA) |
| Native Area | Europe |
| Toxicity | Toxic to people, toxic to pets |

When to Plant?
This will be determined by your planting zone. There is a final frost date for each area. As a result, you can plan your gardening activities around this date. Check our Frost Dates Across North America: First & Last Frost Dates Chart. However, the date will not be the same for every plant.
How to Plant
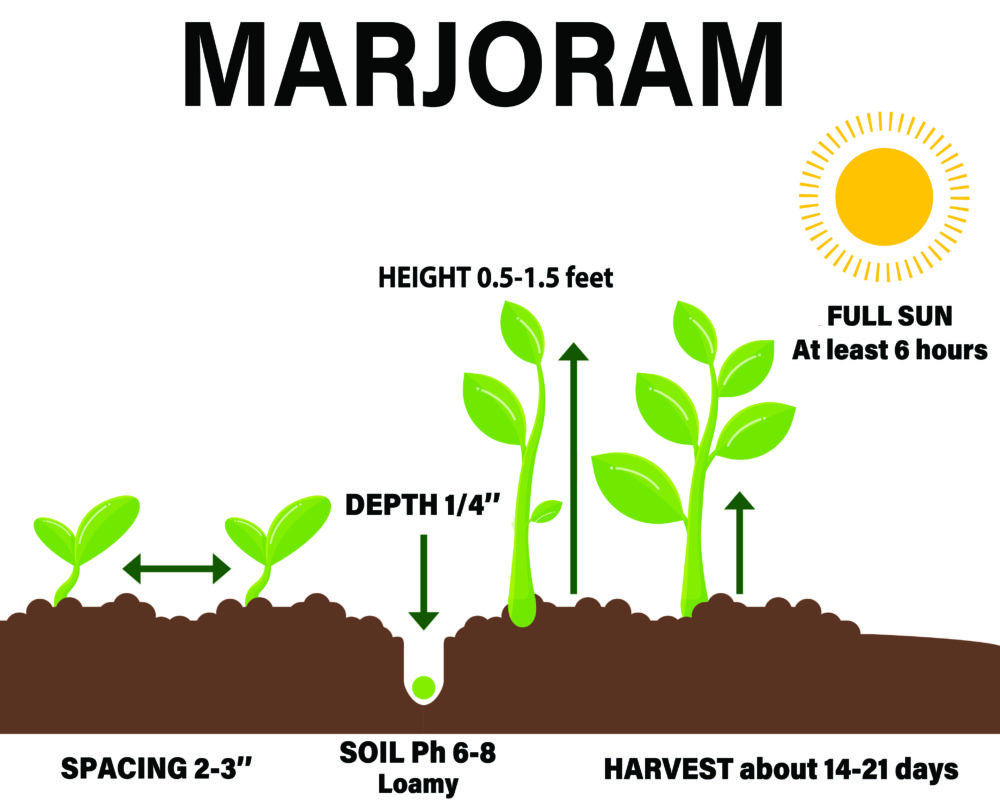
You can take ordinary flowerpots with a capacity of 0.25 – 0.5 gallons for planting marjoram. The pots should have holes at the bottom to drain excess moisture. You can use the other 6 – 8″ deep containers and boxes. Sow seed indoors in early spring.
To speed up germination, soak seeds in water overnight. Cover seeds with a light layer of potting soil and water lightly. Sow marjoram seeds evenly and cover with ¼ inches of fine soil. Firm the soil lightly and keep evenly moist.
Set out seedlings in full sun in slightly alkaline soil that’s rich in organic matter.
Place plants from 2 to 3 inches apart or in clumps of two or three plants set 14 to 22 inches apart. Keep the soil slightly moist until marjoram grows vigorously.
After each harvest, add 1 inch of compost in a 12-inch-wide band around the plants.
Marjoram is a low-growing herb, perfect as a garden edging. It can also be planted in a container or a window box. Marjoram complements almost any fish, meat, dairy, or vegetable dish that isn’t sweet.
Leaves and flowering sprigs of marjoram are popular in Greek and Italian meat dishes, pasta, stuffings, tomato sauces, and soups. Companions – Pepper, Thyme, and Oregano.
How to Cultivate
Soil – Average, well-drained. Marjoram prefers a slightly alkaline soil.
Keep the soil moist at 70°F
For best results, marjoram needs fertile, loamy soil.
This herb prefers a neutral pH of around 6.0 to 8.0.
Sun – Full sun to partial afternoon shade.
Feeding – Not generally needed.
Spacing – 2 – 3″
Water – Water regularly, but do not overwater.
How to Harvest
Harvest the young leaves throughout the growing season and use fresh or freeze for later use.
Gather stems for drying in early summer, just before the plants bloom.
Tie marjoram stems together and hang bunches upside down in a dry, shady, well-ventilated place to make it dry.
After drying, remove leaves from stems and store in an airtight container.
Leaves dry quickly and retain their flavor well.
Hydroponics
Germination: Marjoram seeds can be germinated in a variety of ways, but for hydroponic growing, it’s best to use a seed tray or a nursery pot. Fill the container with a seed-starting mix and moisten it. Sow the seeds on the surface of the soil, and cover them with a thin layer of vermiculite or perlite. Keep the tray or pot in a warm, humid place until the seeds germinate, which usually takes 7 to 14 days.
pH range: The optimal pH range for marjoram is between 6.0 and 7.0. It’s important to regularly monitor the pH level of your hydroponic solution and adjust it as necessary using pH up or pH down solutions.
EC: The ideal electrical conductivity (EC) range for marjoram hydroponics is between 1.2 and 2.2 mS/cm. This measurement indicates the concentration of dissolved salts and nutrients in the hydroponic solution. It’s important to regularly monitor and adjust the EC level to ensure that your plants are receiving the right amount of nutrients.
PPM: Parts per million (PPM) is another way to measure the concentration of dissolved salts and nutrients in the hydroponic solution. The ideal PPM range for marjoram is between 800 and 1500. You can use a TDS (total dissolved solids) meter to measure the PPM level of your solution.
Humidity: Marjoram requires a humid environment to grow well. The optimal humidity range for marjoram is between 50% and 70%. You can maintain the humidity level by using a humidifier or by placing a tray of water near your plants.
Light hours: Marjoram needs at least 12 to 16 hours of light per day to grow properly. You can use grow lights or natural sunlight to provide the required light to your plants.
Temperature air: The ideal temperature range for marjoram is between 20°C to 25°C during the day and 15°C to 18°C at night. Make sure to provide adequate ventilation to maintain a consistent temperature and prevent excess humidity.
Temperature water: The temperature of your hydroponic solution should be between 18°C and 21°C. It’s important to regularly monitor the water temperature to prevent root rot and other issues.
By following these guidelines, you should be able to successfully grow marjoram hydroponically. Good luck!