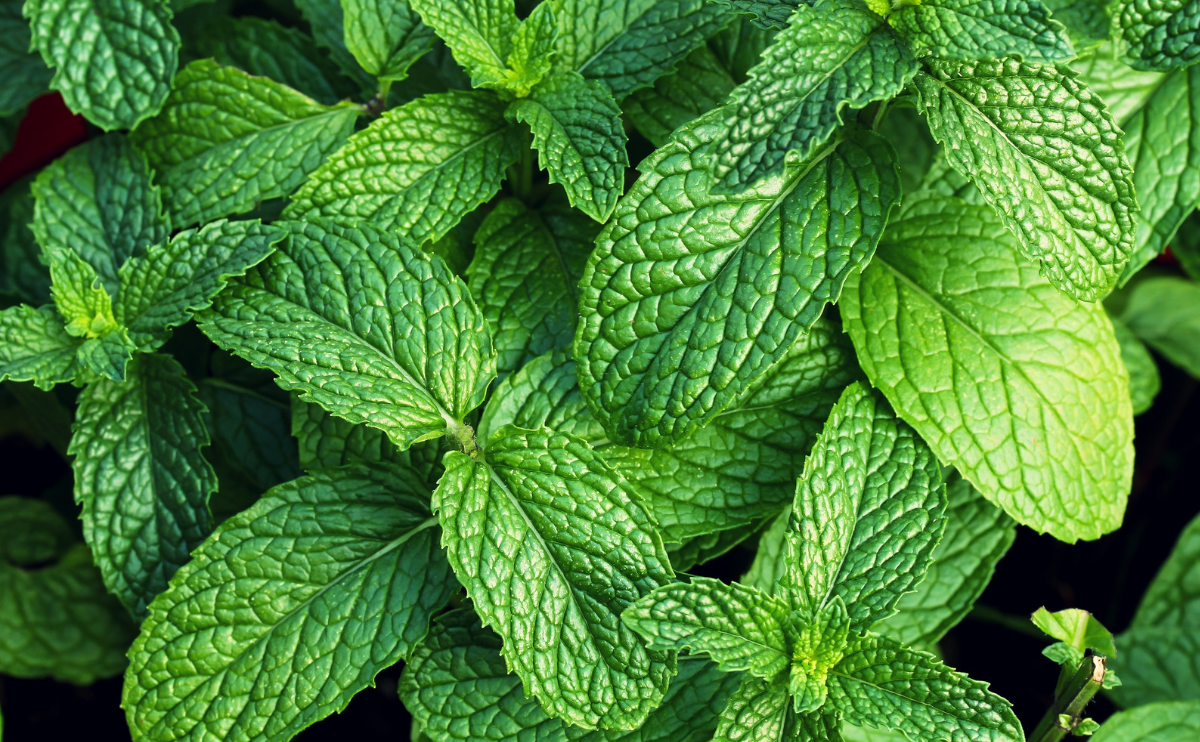
Mint species (Mentha spp.) are very hardy perennials that are simple to identify not just because of their fresh and spicy scent but because all members of the mint genus have opposite leaves and square stems. Long stems grow upward, flop over, and roots will form where the stems touch the soil enabling the mint plant to spread quite aggressively. Its small white or purple summer-blooming flowers attract bees, butterflies, and other pollinators. Mint plants grow quickly and should be planted in the spring after the threat of frost has passed. Mint is toxic to animals if it is ingested.

| Common Name | Mint |
| Botanical Name | Mentha spp. |
| Family | Lamiaceae |
| Plant Type | Perennial, herb |
| Size | 12–18 in. tall, 18–24 in. wide |
| Sun Exposure | Full, partial |
| Soil Type | Loamy, moist, well-drained |
| Soil pH | Acidic, neutral |
| Bloom Time | Summer |
| Hardiness Zones | 3–11, USA (depends on species) |
| Native Area | North America, Africa, Australia |
| Toxicity | Toxic to animals |

When to Plant?
This will be determined by your planting zone. There is a final frost date for each area. As a result, you can plan your gardening activities around this date. Check our Frost Dates Across North America: First & Last Frost Dates Chart. However, the date will not be the same for every plant.
How to Plant
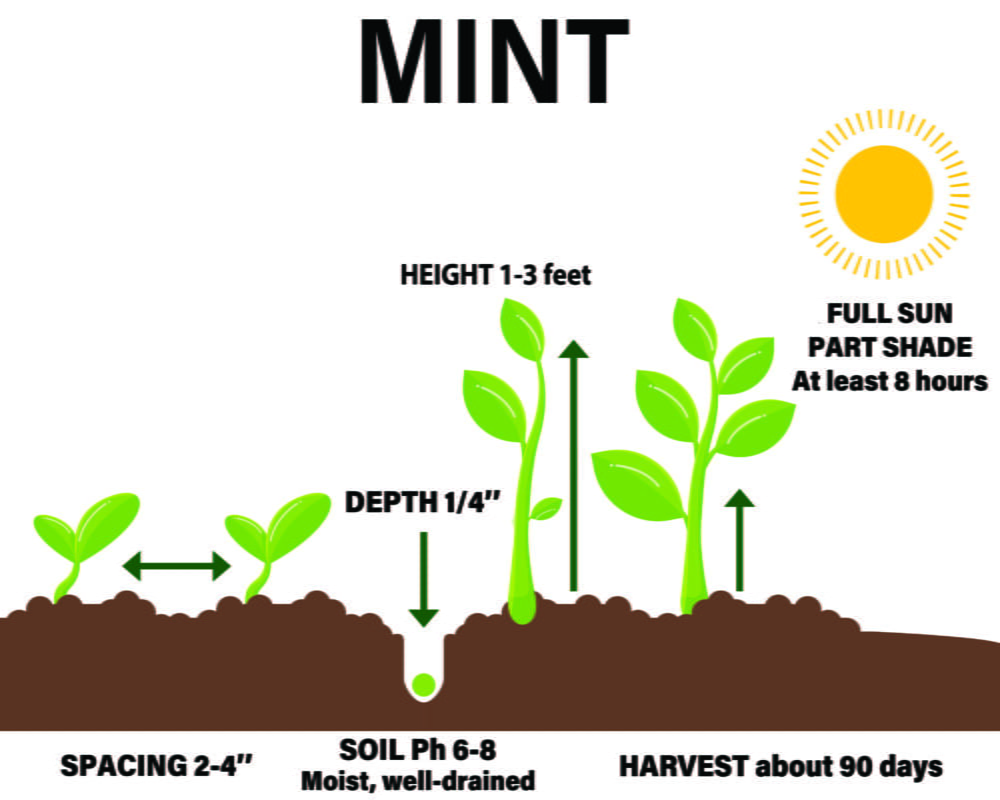
To plant mint seeds, you need from 0.25 to 0.5-gallon pot or a large container at least 6″ deep to ensure that the mint shoots can grow 4″ apart.
A container for growing mint must necessarily have drainage holes. Plant mint in well-drained, fertile soil with direct sunlight for at least 6 – 8 hours a day.
For spring planting, mint seeds can be started indoors in late winter or direct-sown in the warm spring soil. As a hardy perennial, mint seeds can be sown outdoors anytime until about two months before the first frost of fall or year-round indoors. The seeds are spread out on the surface at a distance of 1.5 – 2″ from each other and then slightly sunken. The container should be watered and removed to a warm place. After 2 – 3 weeks, the seeds germinate.
Do not cover the seeds. They need light to germinate. They should sprout within 14 to 20 days at room temperature 70°F. Mint is easy to grow in almost any average to fertile, well-drained soil, in full sun or part shade.
Mint is a perennial with very fragrant, toothed leaves and tiny purple, pink, or white flowers. It has a fruity, aromatic taste. A native plant, Blunt mountain mint, has a natural range from Texas to Illinois, then East to the Atlantic Ocean and New England. Leaves can be used to make mild tea. Native Americans used this plant to treat fevers, colds, stomach aches, and other minor physical ailments. This plant is very dense with leaves and flowers, making it a great choice for manicured flower beds and wildflower gardens. This plant has a very high value for pollinators. Mountain Mint is a favorite flower of bees and butterflies. If you’re looking to increase pollination in your garden or sustain our important neighborhood pollinators, this is a sure bet.
How to Cultivate
Soil – It prefers moist, well-drained soil but can grow in clay.
Sun – Full sun to part shade
Spacing – 2 – 4″
Water – Moist to dry (it’s adaptable)
Let the soil dry out completely before watering.
Fertilizer – This plant has no special fertilizing needs
How to Harvest
The first mint sprouts appear in about 2 – 3 weeks, and they need to be cut off after full germination after three months.
Clip leaves or branches as needed throughout the year.
Mint is so hardy and tough that it will grow right back.
Dry the leaves and flowers for peppermint tea, or use them fresh.
The flowers are edible and make salads and sweets come to life.
Hydroponics
Germination: Mountain mint seeds can be germinated in a seedling tray filled with hydroponic growing media, such as rockwool cubes or coco coir. The seeds should be planted about 1/4 inch deep and kept moist until they sprout, which typically takes 1-2 weeks.
pH range: The pH range for hydroponic Mountain mint should be between 6.0-7.0. Maintaining the correct pH level is important for the plants to absorb the necessary nutrients.
EC: Mountain mint can tolerate a wide range of electrical conductivity (EC) levels, but a general guideline is to maintain an EC between 1.2-2.5 mS/cm.
PPM: The parts per million (PPM) for hydroponic Mountain mint should be around 500-1000 ppm. This measures the concentration of nutrients in the water solution.
Humidity: The humidity level should be maintained at around 50-70% for Mountain mint to grow properly. This can be achieved by using a humidifier or by placing a tray of water near the plants.
Light hours: Mountain mint requires at least 6-8 hours of light per day to grow properly. Ideally, provide 12-16 hours of light per day using a grow light with a spectrum suitable for vegetative growth.
Air temperature: Mountain mint grows best in temperatures between 65-75°F (18-24°C). Keep the air temperature in your growing area within this range using a heater or air conditioning unit if necessary.
Water temperature: The water temperature in your hydroponic system should be maintained between 65-75°F (18-24°C). Use a water heater or chiller to adjust the water temperature as needed.
By following these guidelines, you should be able to successfully grow Mountain mint hydroponically. Good luck with your growing!