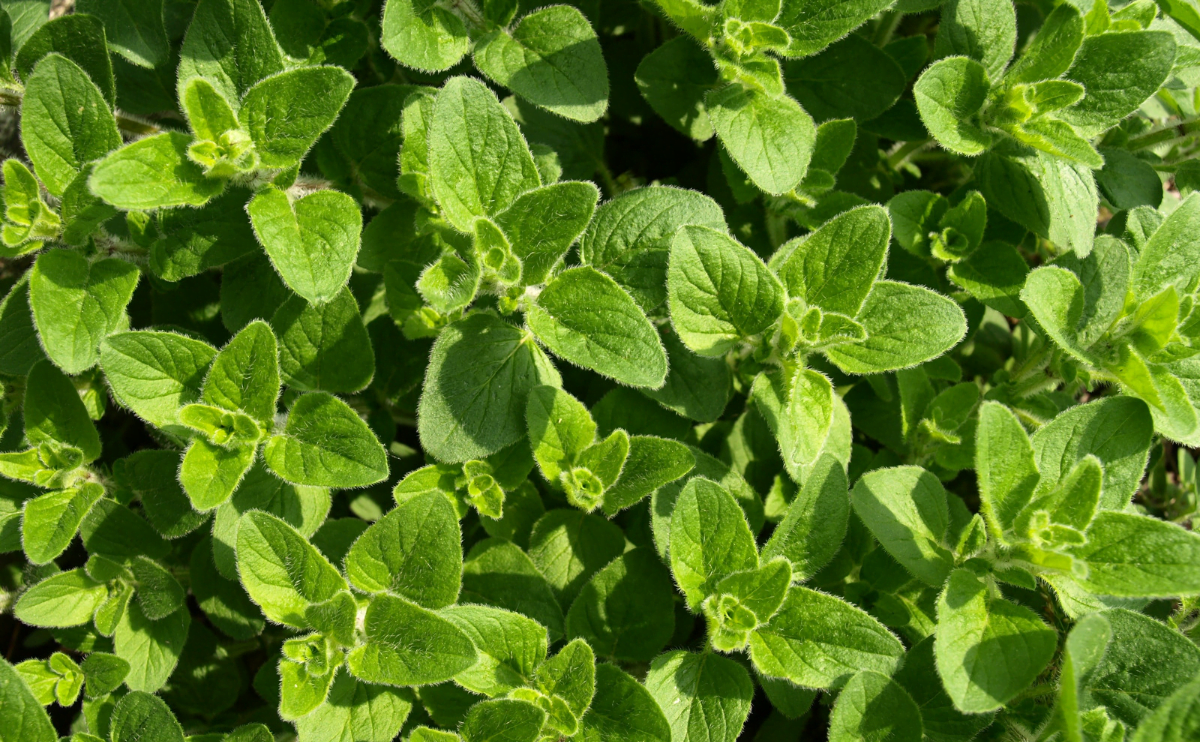
The Oreganum genus contains many perennial herbs and subshrubs that are native to western Asia and the Mediterranean region, though some have naturalized in North America. The most common species are familiar culinary herbs, including Origanum vulgare and Origanum majorana. Oregano leaves are generally oval, dark green, and positioned in opposite pairs along the stems. Some varieties have fuzzy leaves.
Oregano starts as a ground-hugging rosette of leaves, but it can easily grow to about 2 feet tall. It’s generally planted in the spring and grows quickly, providing leaves suitable for cooking almost immediately. Note that oregano is toxic to pets, so be mindful of where you plant it.

| Common Name | Oregano |
| Botanical Name | Origanum spp. |
| Family | Lamiaceae |
| Plant Type | Perennial, herb |
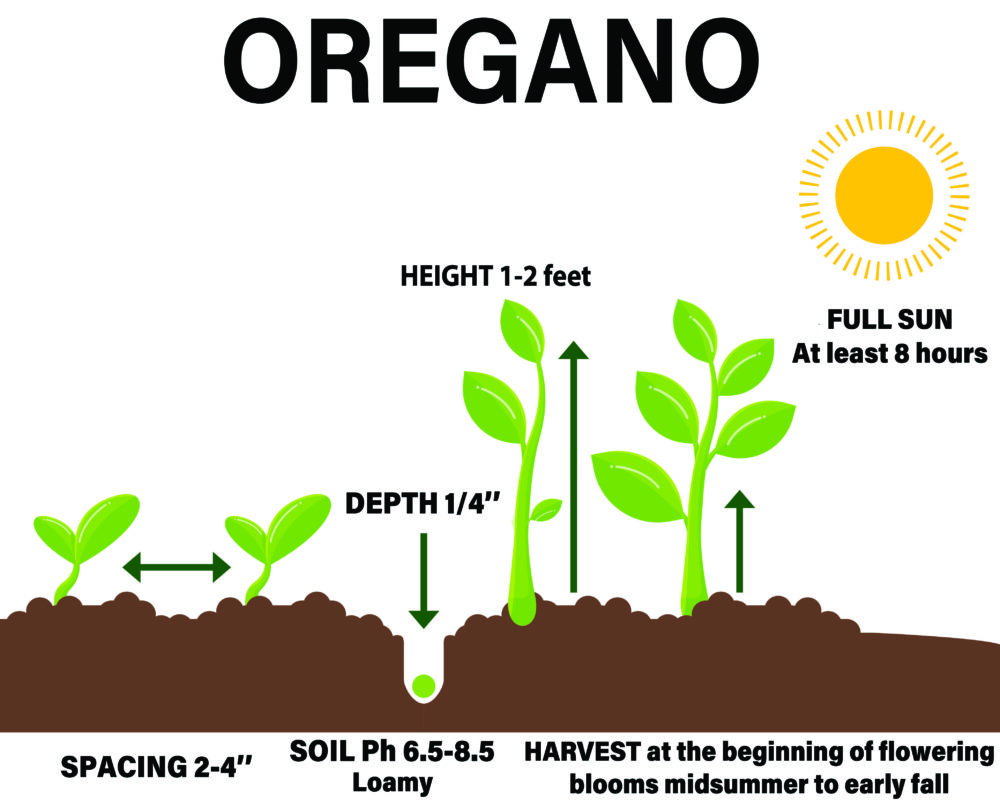
| Size | 1–2 ft. tall, 1.5 ft. wide |
| Sun Exposure | Full sun |
| Soil Type | Well-drained |
| Soil pH | Acidic, neutral |
| Bloom Time | Summer |
| Hardiness Zones | 4–10 (USDA) |
| Native Area | Europe, Asia, Mediterranean |
| Toxicity | Toxic to pets |

When to Plant?
This will be determined by your planting zone. There is a final frost date for each area. As a result, you can plan your gardening activities around this date. Check our Frost Dates Across North America: First & Last Frost Dates Chart. However, the date will not be the same for every plant.
How to Plant
The planting container capacity should be at least 0.5 – 1 gallon.
The small pot can be taken. It has to be up to 3 – 4″ deep.
Oregano grows better in moderately fertile soil, so no fertilization or addition of compost is necessary.
Plant seeds outdoors about six weeks before the last frost.
The soil should be around 70°F.
Avoid overwatering, or the roots may rot.
Oregano is a perennial herb with rose-purple or white flowers and a taste reminiscent of thyme. Oregano is often used in Italian and Spanish cuisines. Oregano leaves are used fresh or dried to flavor many cooked foods, including tomatoes, sauces, salad dressings, and marinades for grilled meats. Oregano is a low-maintenance herb, and it grows well both in the garden or indoors when given the right conditions. Companions – Broccoli, Pepper, and Tomato.
How to Cultivate
Soil – Any average, well-drained soil
Sun – Full sun to partial afternoon shade.
Spacing – Plant oregano 8 to 10 inches apart in your garden.
Water – Don’t overwater oregano. Water thoroughly, only when the soil is dry to the touch.
Fertilizer – Not generally needed.
Frost tolerant – Hardy in cold climates, provided the plant is well-rooted and mulched.
How to Harvest
Oregano can be harvested anytime once they have reached 5 to 7 inches tall.
Harvest the leaves as you need them.
The most flavor-filled leaves are found right before the flowers bloom.
You can freeze the leaves to use during the winter.
They can also be dried in a dark, well-ventilated area and stored in airtight containers until ready to use.
Hydroponics
Germination: Oregano seeds can be germinated in a seedling tray filled with hydroponic growing media, such as rockwool cubes or coco coir. The seeds should be planted about 1/4 inch deep and kept moist until they sprout, which typically takes 1-2 weeks.
pH range: The pH range for hydroponic oregano should be between 6.0-7.0. Maintaining the correct pH level is important for the plants to absorb the necessary nutrients.
EC: Oregano prefers a low to medium electrical conductivity (EC) level, with a general guideline of maintaining an EC between 1.2-2.2 mS/cm.
PPM: The parts per million (PPM) for hydroponic oregano should be around 600-1200 ppm. This measures the concentration of nutrients in the water solution.
Humidity: The humidity level should be maintained at around 40-60% for oregano to grow properly. This can be achieved by using a humidifier or by placing a tray of water near the plants.
Light hours: Oregano requires at least 6-8 hours of light per day to grow properly. Ideally, provide 12-16 hours of light per day using a grow light with a spectrum suitable for vegetative growth.
Air temperature: Oregano grows best in temperatures between 60-75°F (15-24°C). Keep the air temperature in your growing area within this range using a heater or air conditioning unit if necessary.
Water temperature: The water temperature in your hydroponic system should be maintained between 60-70°F (15-21°C). Use a water heater or chiller to adjust the water temperature as needed.
By following these guidelines, you should be able to successfully grow oregano hydroponically. Good luck with your growing!
Common Pests and Diseases
Mint rust (Puccinia menthae)
Symptoms: Small, dusty, bright orange, yellow or brown pustules on undersides of leaves; new shoots may be pale and distorted; large areas of leaf tissue die and leaves may drop from plant
Cause: Fungus
Management
Infected plants and rhizomes should be removed to prevent spread; heat treatment of roots may help to control the disease; roots should be immersed in hot water at 44°C (111°F) for 10 minutes, cooled using cool water and then planted as usual