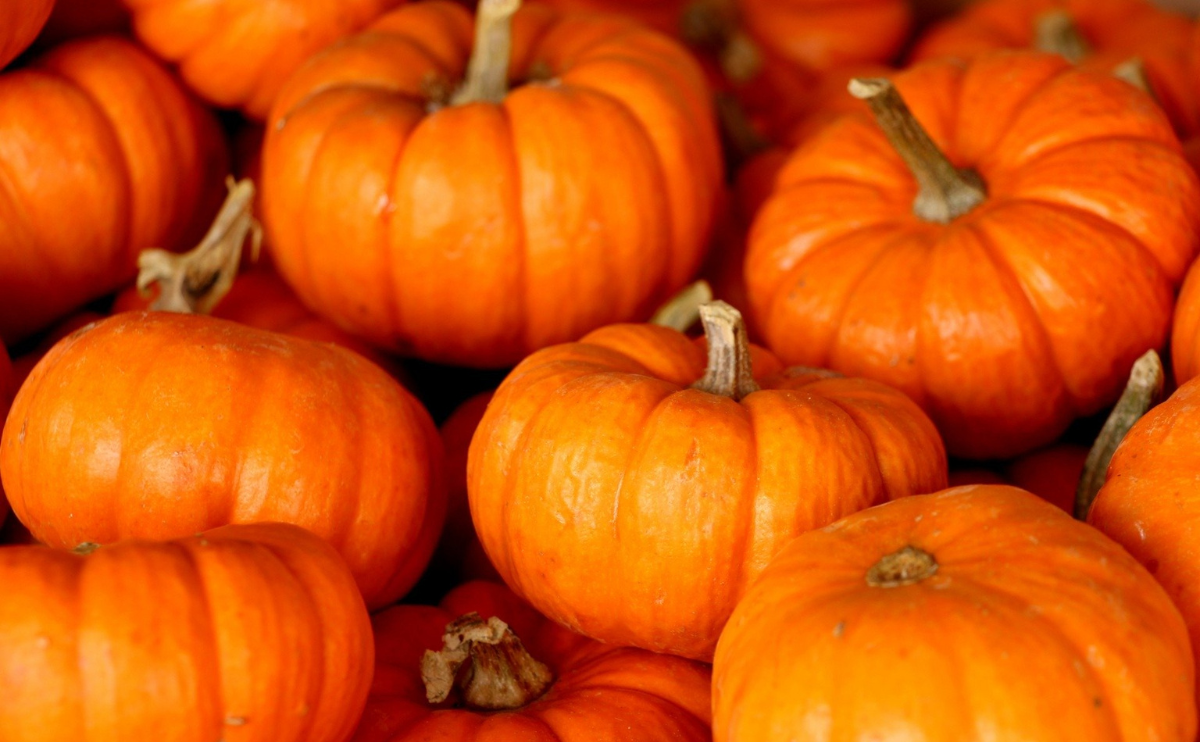
Pumpkin (Curbita spp.) is an iconic plant in North American gardens, a form of squash that symbolizes autumn through its use in creative Halloween jack-o-lantern carvings or as an ingredient for delicious holiday meals. While most people think of a pumpkin as a large, spherical orange fruit with a ribbed rind, various pumpkins also come in colors including white, red, pink, and blue, and with rinds that can be smooth, bumpy, oval, flattened, or round.
All pumpkins are a type of winter squash, but some are simply grown as decoration. Most home-grown pumpkins are cultivars or hybrids of the Curbita pepo species, but there are also other pumpkin species you may run across, including C. maxima, C. argyrosprema, and C.moschata. The species readily cross-pollinate, and many commercial varieties are carefully developed hybrid types.
Like most squash, pumpkin is a low-growing vining annual with large, coarse leaves. The plants flower with yellow blooms in July and August, producing rapidly growing fruits that are left to ripen on the vine for the fall harvest.
Pumpkins require quite a long period of frost-free weather (75 to 120 days) to mature, and they also need warm soil temperatures (at least 60 degrees Fahrenheit) for the seeds to germinate. For this reason, they are typically seeded into the garden as soon as the soil is sufficiently warm in the spring. In regions without the necessary long growing season, pumpkins are often started from seeds indoors two to four weeks before the last spring frost.

| Common Name | Pumpkin |
| Botanical Name | Curbita spp. |
| Family | Cucurbitaceae |
| Plant Type | Annual, fruit |
| Size | 9-18 in. tall, 20-30 ft. long, 10-15 ft. spread |
| Sun Exposure | Full sun |
| Soil Type | Moist, loamy |
| Soil pH | Acidic |
| Bloom Time | Summer |
| Hardiness Zones | 3-9 (USDA) |
| Native Area | North America |

When to Plant?
This will be determined by your planting zone. There is a final frost date for each area. As a result, you can plan your gardening activities around this date. Check our Frost Dates Across North America: First & Last Frost Dates Chart. However, the date will not be the same for every plant.
How to Plant
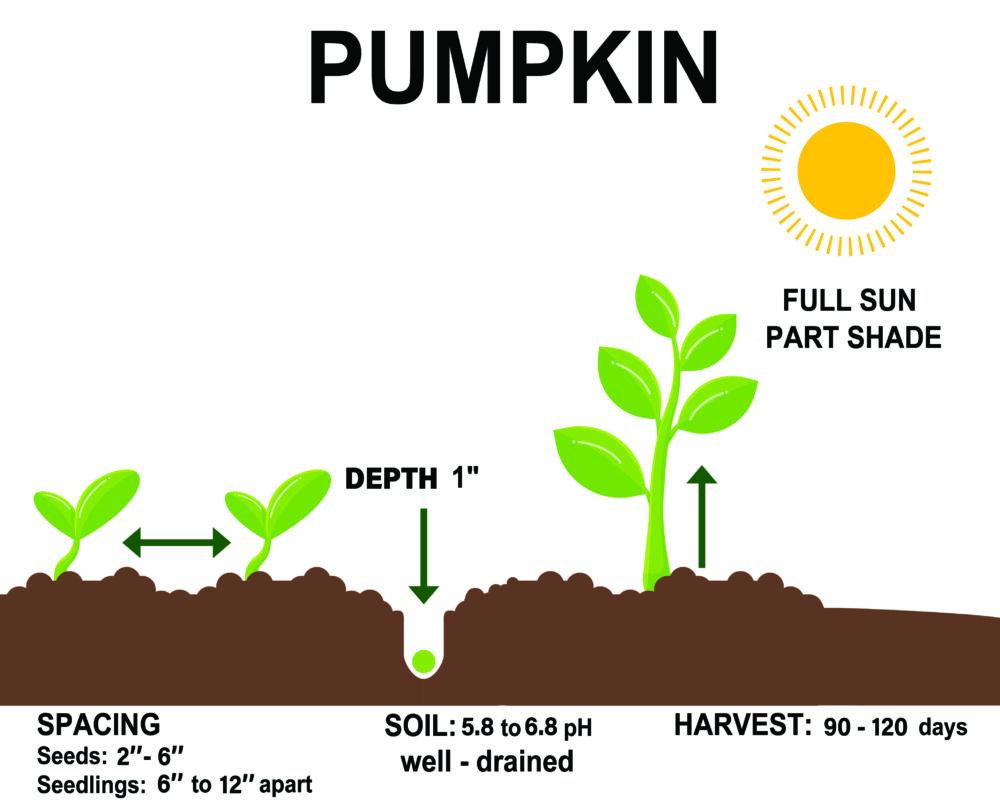
Pumpkin prefers fertile, well-drained, loose soils with a high organic matter content and a pH of 5.8 to 6.8.
From the moment the shoots appear until the fruit begins to bloom, constant, abundant moisture is needed but overwatering should be avoided.
Pumpkins grow on vines that can stretch up to 8 feet or more.
Take your time to plant the pumpkin in early spring. It is very sensitive to frost and prefers warm soil.
Wait until the danger of frost has passed and the soil has warmed up to 60°F – 75°F. Aim seeds 1 inch deep into rows or hills. Sow approximately 4 to 5 seeds per hill. Hills should be spaced 4 to 8 feet apart.
After the plants reach 2 – 3 inches in height, thin up to 2 – 3 plants per hill. While cutting off unwanted plants, try not to touch the roots of the remaining pumpkins. Plant seedlings 6 – 12 inches apart and 6 – 10 feet apart in rows. Thin up to one plant every 18 to 36 inches. For an early harvest, plant pumpkins indoors in 2 – 3 – inch pots or cages 3 – 4 weeks before transplanting outdoors. Sow 3 or 4 seeds into a pot. Cut off the weaker pumpkins without damaging the roots of the remaining ones. When the danger of frost is over, plant the garden’s seedlings outdoors using the abovementioned distances.
Black plastic mulch speeds up plant growth, especially in the cool climate. Don’t forget that mulching your vegetable garden can prevent weeds and retain moisture in the soil.
How to Cultivate
Water – Pumpkins require a lot of water – about 1″ per week. You will need to keep the soil evenly moist, but you want to keep water off of the leaves, so be sure not to use an overhead sprinkler for irrigation. Use a garden hose equipped with a misting nozzle to water the mounds lightly.
Soil – 5.8 to 6.8 pH, well-drained, high fertility
Spacing – seeds – 2″ – 6″
Seedling – 6″ – 12″
Seed life: 6 years
Sun: Full sun/part shade
Germination: 5 – 10 days, 60°F – 105°F
Day to Harvest: 90 – 120 days
How to Harvest
How to tell whether a pumpkin is ripe? It is very simple: you need to knock on it and examine its peel. If the pumpkin makes a dull sound when hit, it can be harvested.
If you press your fingernail on a ripe pumpkin, it should resist punctures because, by the time it ripens, the skin becomes very hard.
To collect the pumpkin, you need to cut the fruit from the vine with scissors or a sharp knife while leaving the pumpkin’s long handle.
Hydroponics
Germination: Start by selecting pumpkin seeds that are viable and healthy. Soak the seeds in water for a few hours to help speed up germination. Once the seeds have swollen, place them in a germination tray or seedling plugs. Keep the tray moist and cover it with a lid to maintain high humidity levels. Place the tray in a warm location with a temperature range of 21-32°C (70-90°F). The seeds should sprout within 7-10 days.
pH range: The pH range for growing pumpkin hydroponically should be between 5.8 and 6.5. Maintaining a proper pH is essential for nutrient absorption and plant growth. Use a pH meter or pH strips to test the pH level of the nutrient solution.
EC: The Electrical Conductivity (EC) level for pumpkin hydroponic growth should be between 1.5-2.5 mS/cm. EC measures the amount of nutrients in the solution. Too high or too low EC levels can harm the plant’s growth.
PPM: The Parts Per Million (PPM) level for pumpkin hydroponic growth should be between 1000-1500 ppm. PPM measures the amount of dissolved solids in the nutrient solution. Too high or too low PPM levels can also harm the plant’s growth.
Humidity: The humidity levels should be kept high during the germination stage, around 70-80%. Once the plants have grown, maintain the humidity levels around 60-70% during the vegetative stage and 50-60% during the fruiting stage.
Light hours: Pumpkins need at least 8-10 hours of direct sunlight each day. If you are growing your pumpkins indoors, you can use LED grow lights to provide the necessary light for photosynthesis.
Temperature air: The ideal temperature range for growing pumpkins hydroponically is between 18-25°C (65-80°F) during the day and between 13-18°C (55-65°F) at night. Make sure to provide good ventilation to avoid the temperature getting too high or too low.
Temperature water: The ideal temperature range for the nutrient solution should be between 18-21°C (65-70°F). Avoid temperatures above 25°C (77°F) as it can reduce oxygen levels and affect plant growth.
With these guidelines, you should be able to grow healthy plants hydroponically. Good luck, and happy growing!